Table of Contents
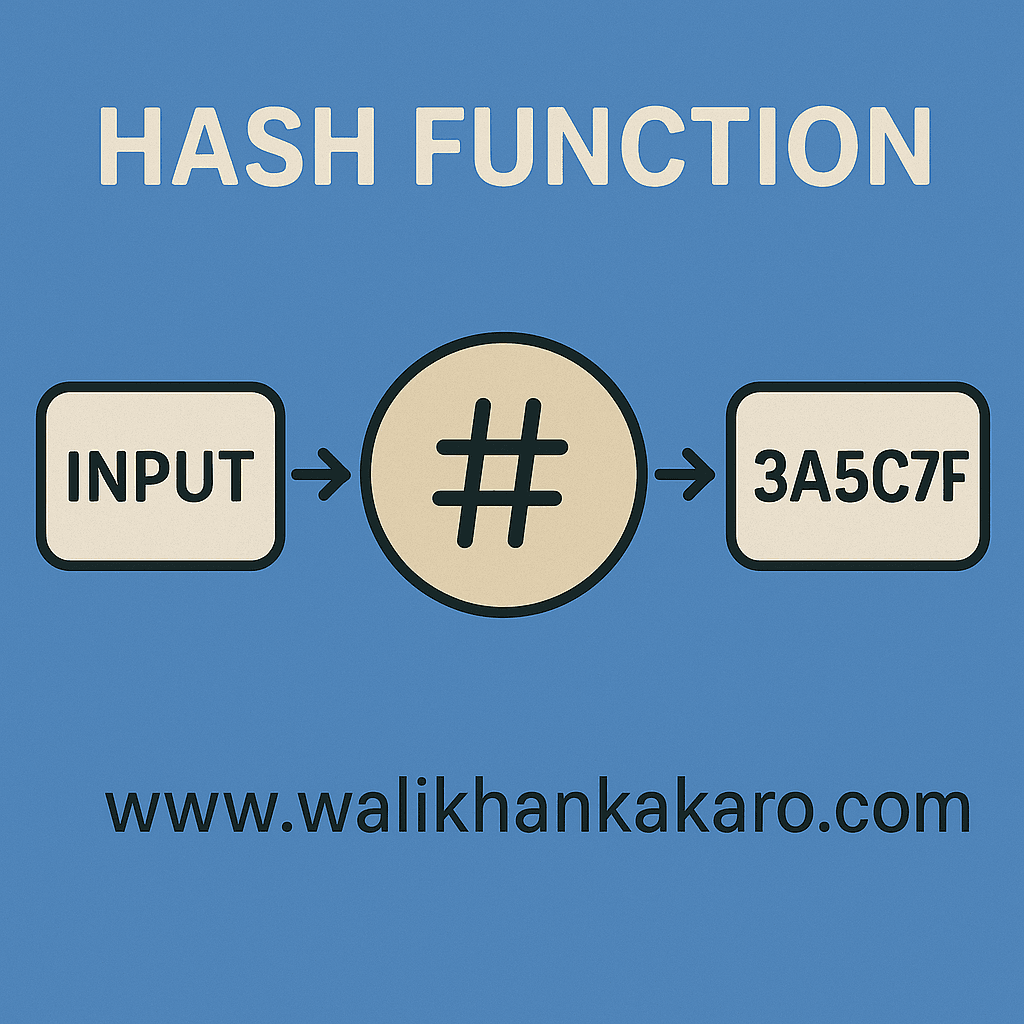
A Hash Function is a mathematical algorithm that converts input data of any size into a fixed-length string, known as a hash value or digest.
Hash functions are widely used in cryptography for ensuring data integrity, storing passwords, and creating digital signatures.
They are designed to be fast, deterministic, and collision-resistant, ensuring that even a small change in input produces a completely different hash output. Popular hash algorithms include MD5, SHA-1, and SHA-256.
Hash Function
1: One Way Process.
2: Confidentiality and Integrity.
3: Password Storage.
4: Biometric Data.
5: Unique String.
6: Fixed Length.
7: Specific Characters.
8: Salt Characters.
9: Comparison.
10: Rainbow Table.
11: Checksum.