Table of Contents
Cyber security Quiz with answers
1: Sudo: Super User Do.
2: Apt: Advanced Package Tool.
3: PING: Packet Inter-Network Groper.
4: What is Ping?
Answer: Ping tests the network communication between two devices.
5: Penetration testing tools.
1: Wireshark.
2: Burp Suite.
3: Nessus.
4: Metasploit.
6: What are the stages involved in penetration testing.
1: Information Gathering.
2: Reconnaissance.
3: Discovery and Scanning.
7: Explain “Stride”.
Answer: Stride identify a thread modeling technique.
1: Spoofing.
2: Tampering.
3: Repudiation.
4: Information disclosure.
5: Denial of Service (Dos).
6: Elevation of privilege.
8: What is the full form of the following terms 2FA, 2S2D, 2VPCP, 3DES, 3DESE, and 3DESEP?
Answer:
1: 2FA: Two Factor Authentication.
2: 2S2D: Double-Sided Double-Density.
3: 2VPCP: Two-Version Priority Ceiling Protocol.
4: 3DES: Triple Data Encryption Standard.
5: 3DESE: Triple Data Encryption Standard Encryption.
6: 3DESEP: Triple Data Encryption Standard Encryption Protocol.
9: What are the primary goals of performing a pentesting exercise.
1: Secure confidential data.
2: Detect loopholes in the system.
3: Find vulnerabilities in apps.
4: Assess the impact of cyberattacks on business.
5: Meet the regulatory security compliances.
Apply a strong security strategy.
10: How many types of penetration testing are there?
Answer: The three types of penetration testing are:
1: Black-Box Testing.
2: White-Box Testing.
3: Gray-Box Testing
11: What are the different types of pentesting for mobile applications?
Answer: Some key mobile testing types are:
1: Functional Testing.
2: Performance Testing.
3: Memory Leakage Testing.
4: Interrupt Testing.
5: Usability Testing.
6: Installation Testing.
7: Security Testing.
8: Recoverability Testing.
9: Compatibility Testing.
12: What are Transmission Modes?
Answer: The data is transmitted from one device to another device through a transmission mode. The transmission mode decides the direction of the data in which the data needs to travel to reach the receive system or node.
The transmission mode is divided into three categories:
1: Simplex
2: Half-Duplex
3: Full-Duplex
13: What is Static IP?
Answer: Static IP Address never changes.
14: What is another term used for security weakness?
Answer: Vulnerability
15: SQL Injection is an attack in which Malicious code is inserted into strings that are later passed to an instance of SQL Server.
16: DoS is abbreviated as?
Answer: Denial of Service.
17: Android is based on?
Answer: Linux Kernel.
18: HTTP runs on which port?
Answer: Port 80.
19: rmdir command is used to remove the directory in Linux.
20: Which command is used for executing a shell program?
Answer: ./
21: Command used to check the current network interface.
Answer: ifconfig.
22: Nmap function for Ack scan?
Answer: -sA
23: Which protocol is more difficult for a Network administrator?
Answer: SNMP.
24: Clearing log is the process of?
Answer: Removing all your footprint and activities from a system.
25: Crypter is a Malware.
26: What is the full form of RAT?
Answer: Remote Access Trojan.
27: Sniffing is a data interception method used by hackers.
28: What is the full form of ARP?
Answer: Address Resolution Protocol.
29: What is the full form of the SET tool?
Answer: Social Engineering Toolkit.
30: Metasploit is used for creating an android payload.
31: Classification of Vulnerability.
1: Misconfiguration.
2: Default Installation.
3: Buffer Overflows.
4: Design Flaws.
5: Operating System Flaws.
6: Application Flaws.
7: Open Services.
8: Default Passwords.
32: Need for Cybersecurity?
1: Securing the Internet.
2: Securing the Data.
3: Securing the Personal Info.
4: securing from money loss.
5: Securing from Cyber-attacks and frauds.
33: Domains in Cyber Security?
1: Digital Forensics.
2: Identity and Access Management.
3: Endpoint Security.
4: Risk Management.
5: Security Operations.
6: Threat Intelligence.
7: Cloud Security.
8: Application Security.
34: Cybersecurity basics?
1: System Basics: Hardware, Software, Input, Out, and Processing Methodology.
2: Web and Internet: HTTP, DNS, Web Servers, FTP, and SMTP.
3: Networking: TCP, UDP, IP, ARP, Devices, types, Routing and Switching.
4: Operating System: Linux (Kali, Ubuntu), Windows, Android, iOS, and MAC.
5: Command Line: CMD, Bash, and PowerShell.
35: What is the purpose of the Footprinting?
Answer: Information Gathering
36: What phase comes after Footprinting?
Answer: Network Scanning
37: What are the Footprinting phases?
Answer: Active and Passive
38: Which tool can trace the path of a packet?
Answer: Tracert
39: What is the basic element of the security?
1: Confidentiality.
2: Integrity.
3: Availability.
40: Which saves time and resources, but is not accurate or professional?
Answer: Automated Pentesting
41: Does the risk assessment depend heavily on the vulnerability assessment?
Answer: Ture
42: SQL Injection techniques can be used to find web application vulnerabilities.
Answer: True
43: What is the ethics behind training how to hack a system?
Answer: To think like hackers and know how to defend against such attacks.
44: What is the HTTP port?
Answer: Port 80
45: What is the HTTPS port?
Answer: Port 443
46: Inserting the malicious code in the input fields (like search box) of a vulnerable site to extract sensitive DB (Data Base) information from the server, this attack is called?
Answer: SQL Injection
47: If I hack a system, only after getting written permission from the owner of the system then what I will be called?
Answer: White Hat Hacker
48: OSINT stands for?
Answer: Open-source intelligence
49: Python language can be used to write tools and scripts for ethical hacking?
Answer: True
50: What is Crunch?
Answer: Crunch is a wordlist generator where you can specify a standard character set or any set of characters to be used in generating the wordlists.
51: What is CeWL?
Answer: CeWL (Custom Word List generator) is a ruby app that spiders a given URL, up to a specified depth, and returns a list of words that can then be used for password crackers such as John the Ripper. Optionally, CeWL can follow external links. CeWL can also create a list of email addresses found in mailto links.
52: What is the echo command?
Answer: echo is a command that outputs the strings that are passed to it as arguments.
Example: echo “Hello World!”
53: How to check the Host name in the computer.
Command: hostname
54: Explain the difference between relative path and absolute path?
Answer: Relative path: Start from current working directory.
Absolute path: The full path to a file or directory.
55: Difference between grep and egrep?
Answer: In egrep, you can search for more than one strings at same time.
Example: egrep “key1|key2|key3”
56: What is the advantage of using less command?
Answer: We can easily read big files. Forward and backward search is easy. Navigation from top to bottom is easy.
57: What is root?
Answer: Admin or super use.
Answer: / root home directory for root user.
Answer: / root directory.
58: What is pipe used for?
Answer: Pipe is used to combine two commands and redirect output of command1 to command2.
59: Different ways to access a Linux server remotely (from a Windows machine)?
Answer: Using some tools and terminal like:
1: putty.
2: git bash.
3: cmd.
60: What are different types of permissions for a file in Linux?
Answer: Read (r)
Write (w)
Executable (x)
61: Which permission allow a user to run an executable file(script).
Answer: We need to provide executable (x) permission to the user.
62: How to Automate any task or script?
Answer: Using cron jobs
For which we have crontab and at command.
63: What is the meaning of this cron job? *****
Answer: * (Minute)
** (Hour).
*** (Day of the Month).
**** (Day of the week).
64: If your cron job didn’t work, how would you check?
Answer: check system time,
Crontab entry,
check /var/log/messages
65: What is daemon service?
Answer: Service that keep running in background.
Example: httpd, sshd, and chronyd.
66: What is a process in Linux?
Answer: An instance of a running program.
Whenever you start a program/application or execute a command, a process is created.
For every process a unique no. is assigned which is called PID (Process ID).
67: Difference between kill and kill-9?
Answer: kill-9 will terminate a program forcefully.
68: Difference between Telnet and SSH?
Answer: SSH is secured and telnet is not.
69: Which service should be running on server to allow you to connect remotely?
Answer: ssh or sshd
70: What is SSH?
Answer: SSH or Secure Shell is a network communication protocol that enables two computers/devices to communicate and share data.
71: Why it is called as Secure Shell?
Answer: Because communication between host and client will be in encrypted format.
72: What is default port for SSH?
Answer: 22
73: ls command: This command shows a list of all the file and directories present in the current working directory of your machine.
74: cd command: Change directory command. It is used to change current working directory.
75: pwd command: This command prints the current working directory.
76: mkdir command: The mkdir command allow users to create new directory.
77: touch command: Touch command is a way to create empty files.
78: cat command: Print the content of a file. The cat command also allows us to write some texts into a file. Combine files using cat command.
79: mv command: Moves files from one directory to another directory. Used for renaming a file or directory.
80: wc command: Total number of lines, Total number of words, Total number of characters.
81: sort command: Sort command is used to sort a file.
82: Uniq command: Uniq is the tool that helps to detect the adjacent duplicate lines and also deletes the duplicate lines.
83: history command: History command is used to view the previously executed command.
84: hostname command: Display hostname.
85: hostname -i: Display IP Address of hostname.
86: head command: Display top 10 lines.
87: tail command: Display last 10 lines.
88: tac command: Display in reverse order.
89: rm command: Remove command is used to removes files.
90: rmdir command: Rmdir command is used to remove a directory.
91: chmod command: chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories. User, Groups, Others [r-read, x-execute, w-write].
92: grep command: Global Regular Expression Pattern. This command is used to search text and string in a given file.
93: Explain the difference between passive and active reconnaissance?
1: Passive Reconnaissance: Attacker collects data about a target system or network without directly engaging with it.
Passive reconnaissance is designed to minimize the risk of detection by the target and is primarily focused on obtaining a comprehensive understating of the target’s environment.
2: Active Reconnaissance: Involves engaging with the target system or network directly to gather more detailed information.
Provides deeper insights into the target’s network structure, services, and potential vulnerabilities.
94: How do you distinguish between high-risk and low-risk vulnerabilities and distinguishing high-risk and low-risk vulnerabilities?
High-Risk Vulnerabilities:
High-Risk vulnerabilities are characterized by their potential to cause significant operational, disruptions, data breaches, financial loss, and regulatory non-compliance.
Low-Risk vulnerabilities:
Low-risk vulnerabilities, while still representing security weakness, have a lower potential for exploitation and impact.
Periodization and Risk mitigation:
The goal is to prioritize the vulnerabilities that pose the greatest threat and address them promptly.
Considering factors such as potential business impact, the ease of exploitation, the value of the targeted asset, and regulatory requirements.
95: Which tools would you use for network scanning and why?
Answer: Ultimately, the choice of network scanning tools would depend on the objective to the engagement the available resources, and specific technical requirements of the target network.
1: Nmap (Network Mapper).
2: Nessus.
3: Wireshark.
96: How would you educate clients about the risks of social engineering attacks and ways to prevent them?
Answer:
1: Tailor the message to the audience.
2: Explain common social engineering tactics.
3: Illustrate real consequences.
4: Foster a culture of security.
97: Can you explain the steps you would take to conduct a penetration test on a web application?
1: Reconnaissance.
2: Web application discovery.
3: Vulnerability identification.
4: Exploitations and verification.
5: Reporting.
98: Which device connects multiple network segments and operates at the data link layer of the OSI Model?
Answer: Switch
99: What is IP Address?
Answer: Private IP address beginning with 192.168
100: Which network topology connects all devices in a Linear fashion?
Answer: Bus topology
101: What is the default subnet mask for a class C IP Address.
Answer: 225.225.255.0
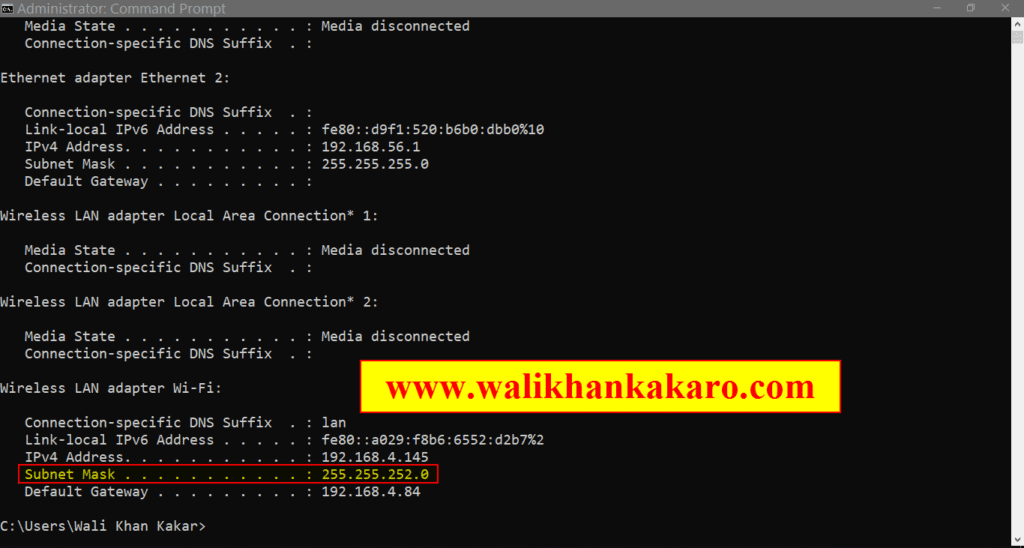
102: DNS cache poisoning, also known as DNS spoofing.
103: What is Handshake protocol?
Answer: Establishes a secure connection between two devices or systems.
104: What is ARP?
Answer: Address Resolution Protocol
105: What is ARP?
Answer: ARP converts IP into MAC Address
106: ARP used IPV4.
107: Command Injection also known as Shell Injection.
108: Port forwarding, also known as port mapping.
109: DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
110: DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses and other configuration information to devices on a network.
111: DHCP ports?
Answer:
1: DHCP server: Uses UDP port 67
2: DHCP client: Uses UDP port 68
112: The old name of Kali Linux was BackTrack Linux.
113: PING stands for Packet Internet Groper.
114: What is the Read, Write and Execute permissions?
Answer: r = 4, w = 2, x = 1
115: What is Sniffing?
Answer:
1: Sniffing is a process of monitoring and capturing all data packets passing through a given network using software or a hardware device.
2: Attacker use sniffers to capture data containing sensitive information such as password, account information, etc.
3: Attacker gain information by reading unencrypted data packets.
116: What are the Packet Sniffing Tools?
Answer:
1: Wireshark.
2: tcp dump
3: Cain and Cable
4: Capsa Network Analyzer
5: Colasoft 117:


