Table of Contents
MySQL table constraints
1: Open the MySQL Workbench.
2: MySQL constraints:
1: NOT NULL
2: UNIQUE
3: DEFAULT
4: CHECK
5: FOREGIN KEY
6: PRIMARY KEY
3: Table without constraints.
| Id | Name | Age | Gender | Phone | Status |
| 1 | A | 17 | M | 3269 | 1 |
| 2 | B | 20 | F | 5862 | 1 |
| 3 | C | 30 | M | 3269 | 1 |
| D | 25 | M | 2039 | 1 | |
| 4 | E | 23 | M | 1096 | 1 |
4: Use a Database.
Code: use walikhankakar;
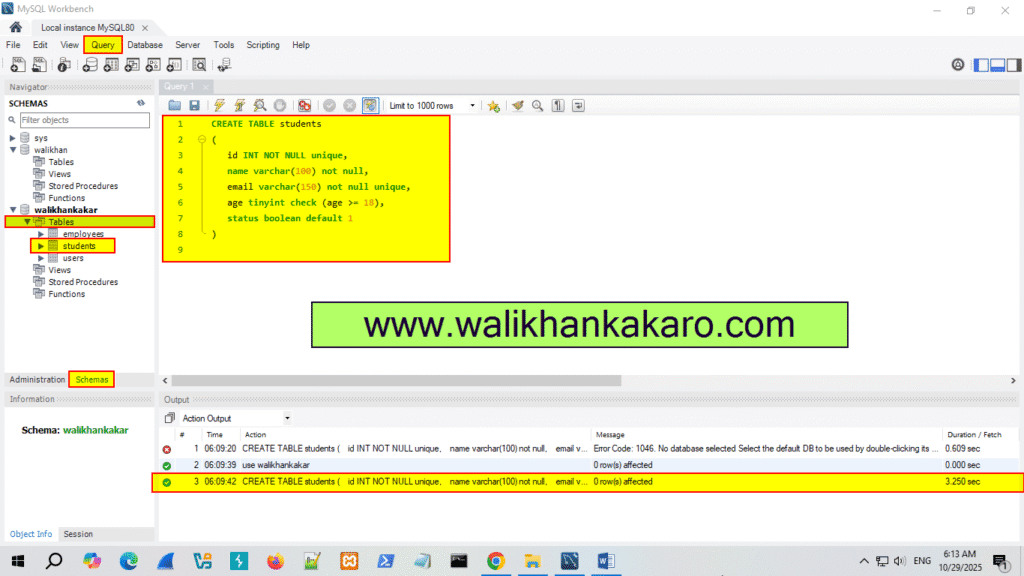
5: Create a new table.
Code: CREATE TABLE students
(
id INT NOT NULL unique,
name varchar(100) not null,
email varchar(150) not null unique,
age tinyint check (age >= 18),
status boolean default 1
)
6: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
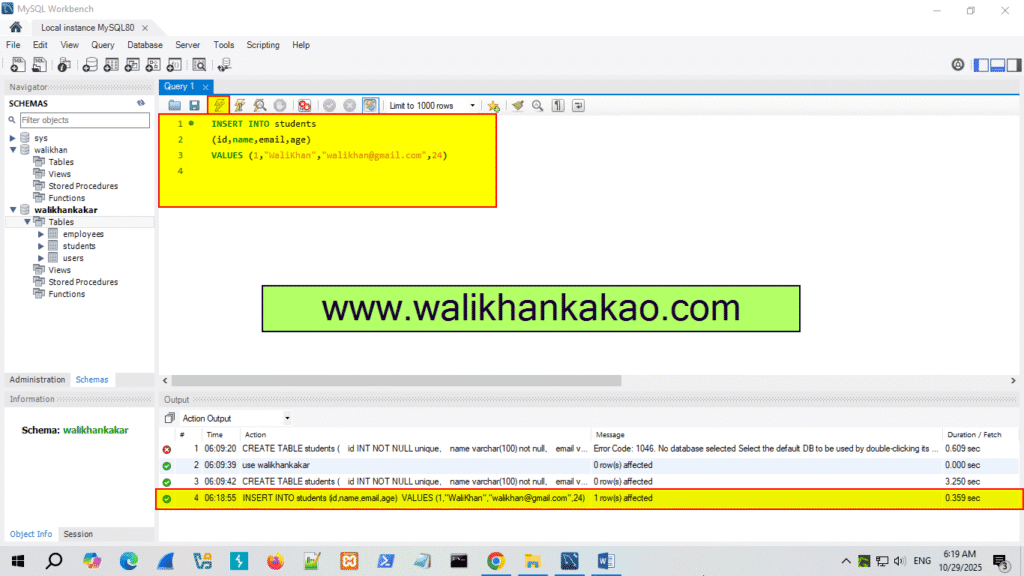
7: Insert the data into the students table.
Code: INSERT INTO students
(id,name,email,age)
VALUES (1,”WaliKhan”,”walikhan@gmail.com”,24)
8: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter