Table of Contents
Programming Languages
MySQL
Install MySQL in Windows
1: Download the MySQL community.
Website: https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/installer/
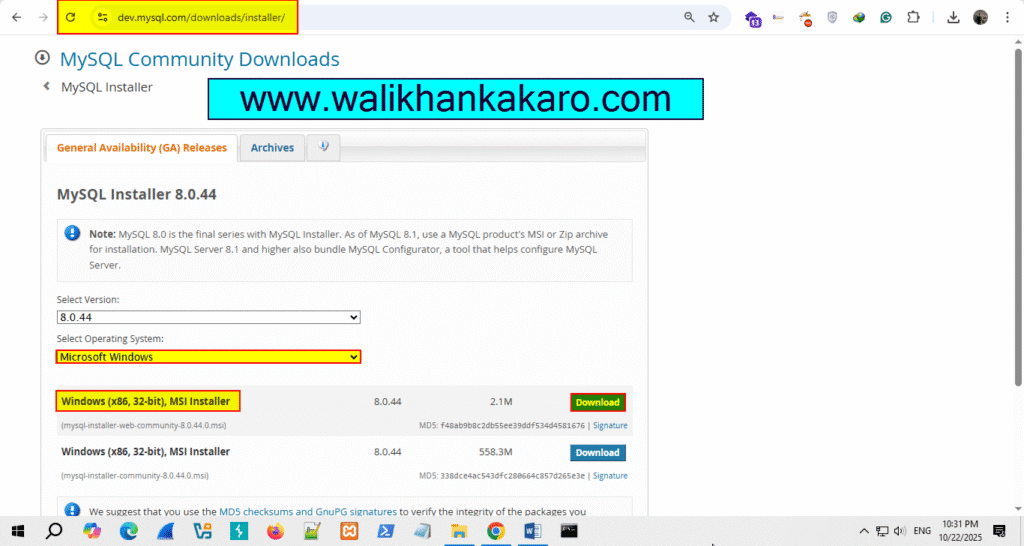
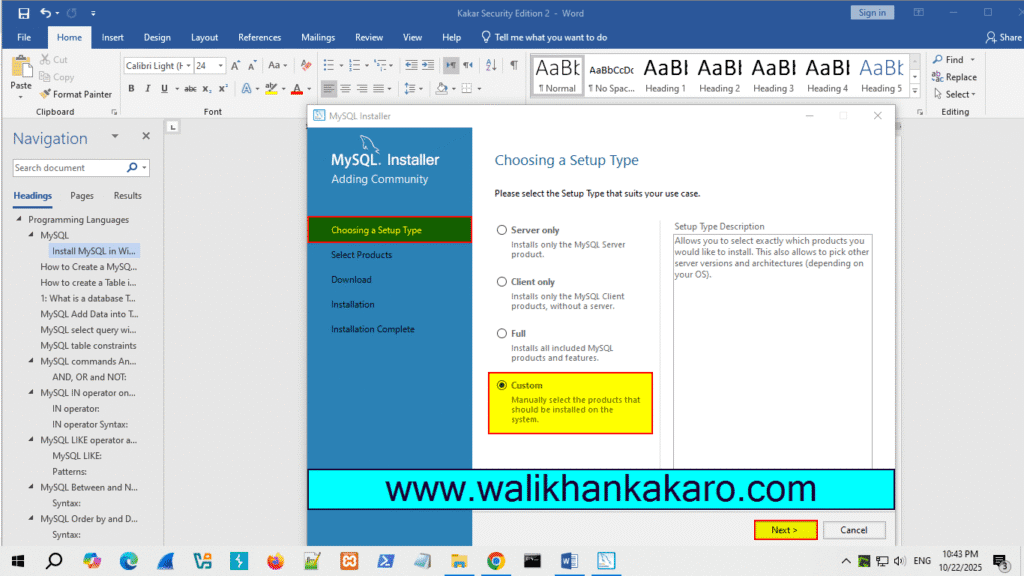
2: Install the MySQL community.
3: Select the Custom option.
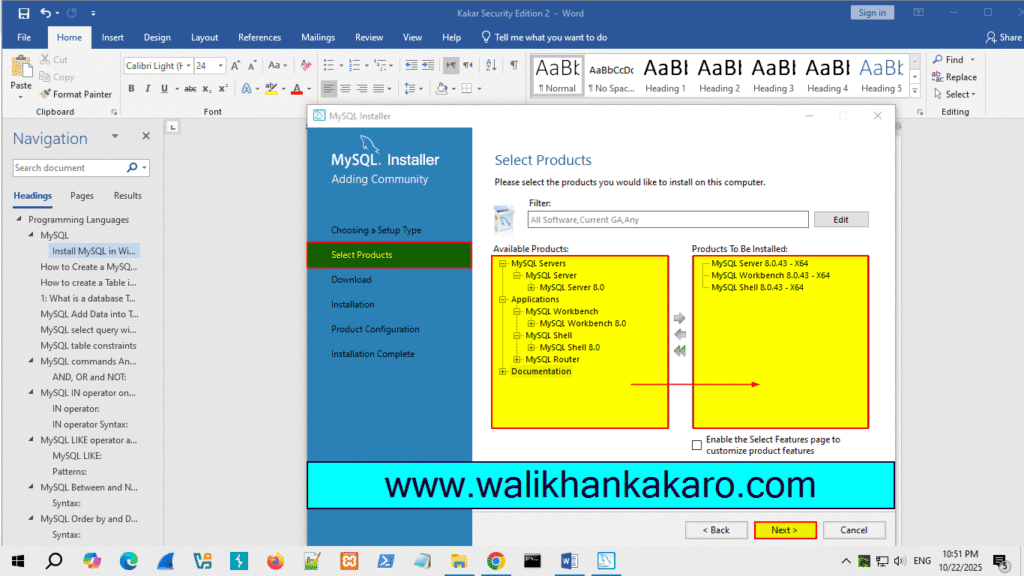
4: Select the Products.
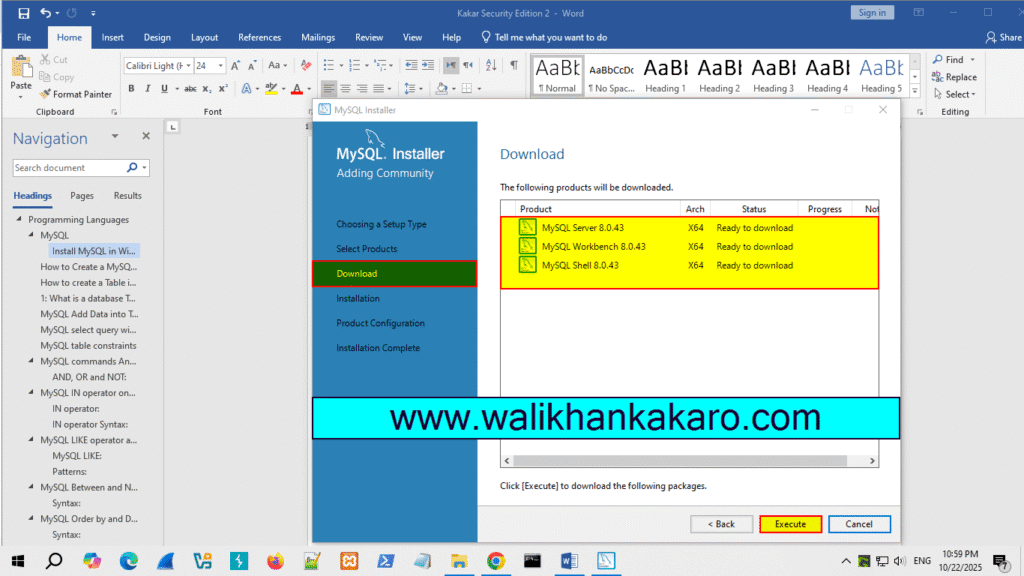
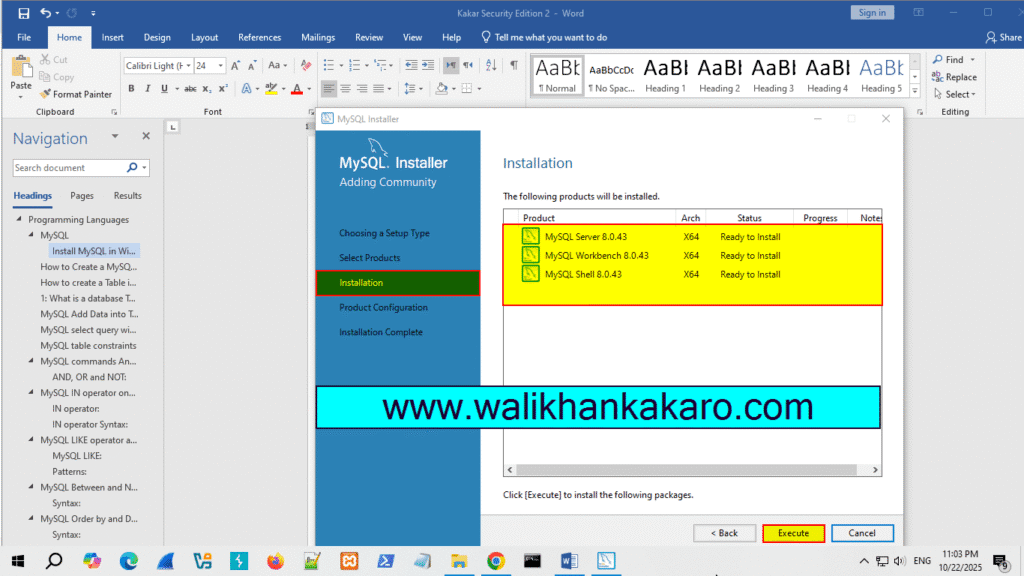
5: Execute the process.
6: Execute the installation process.
7: Off the XAMP server if you installed.
8: Next, Next, Next, and Next the Process.
9: Make a new password.
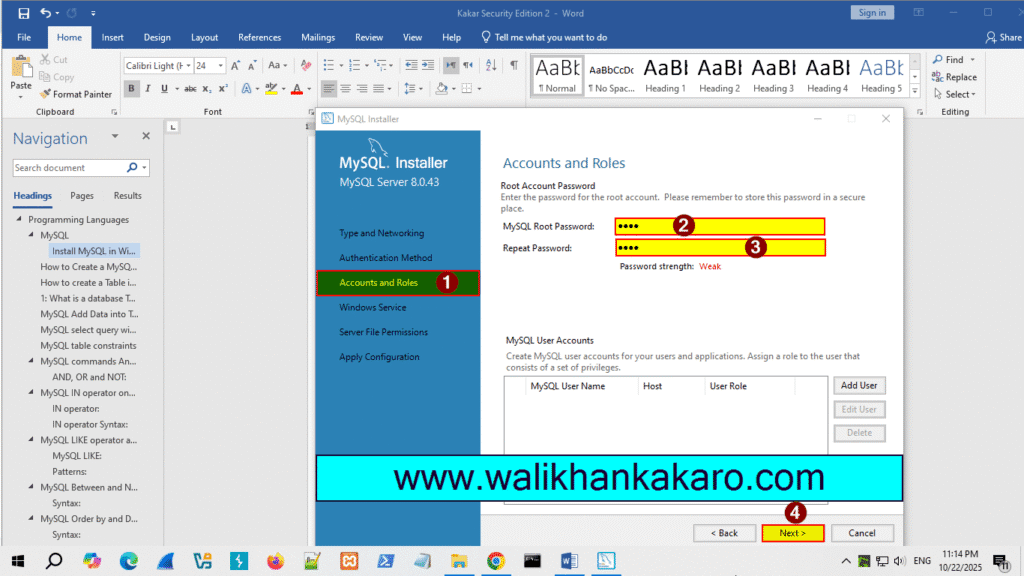
10: Next, and Next the process.
11: Execute the configuration files.
12: Finish the MySQL Installation.
13: MySQL Workbench and MySQL Shell will automatically be launched.
14: Open the MySQL server.

15: Open the Command Prompt.
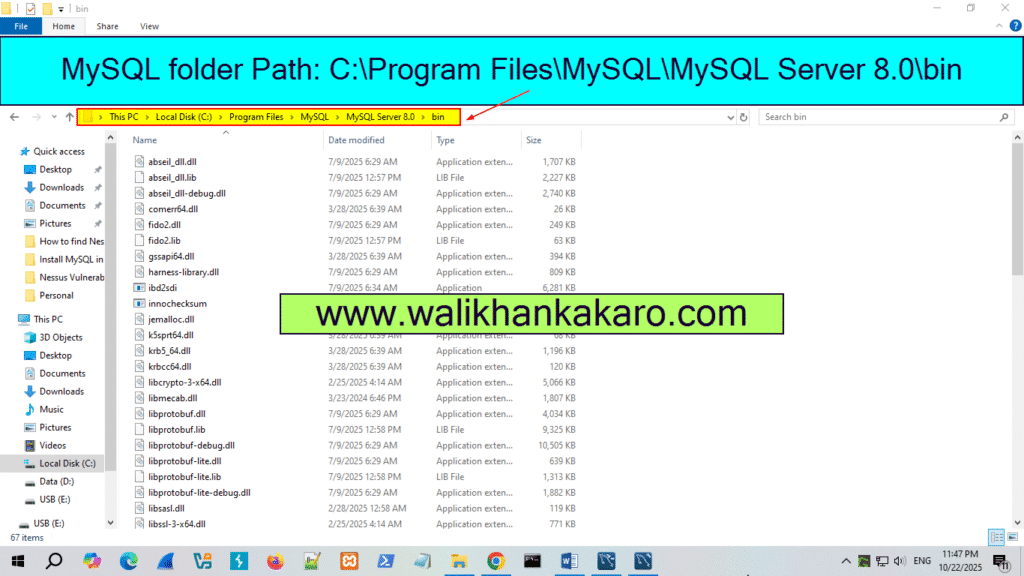
16: Go to the installed MySQL folder.
17: Open the MySQL folder, open the MySQL Server, and then open the bin folder, and then copy the path.
Example: C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server8.0\bin
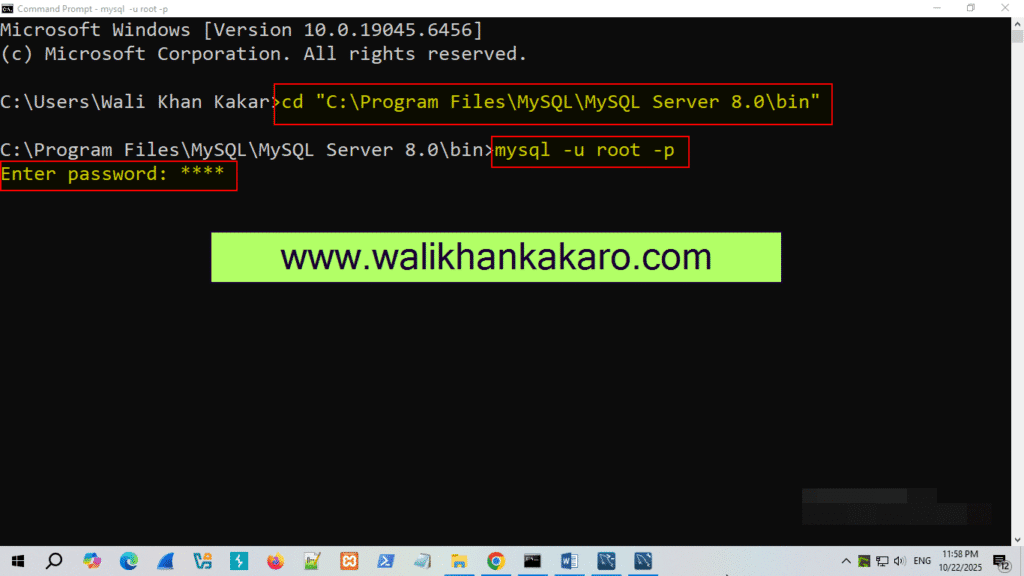
18: Open your server in the Command Prompt.
Command: mysql -u root -p
19: Give your MySQL server password.
20: Check the MySQL default Databases in the Command Prompt.
Command: show databases;
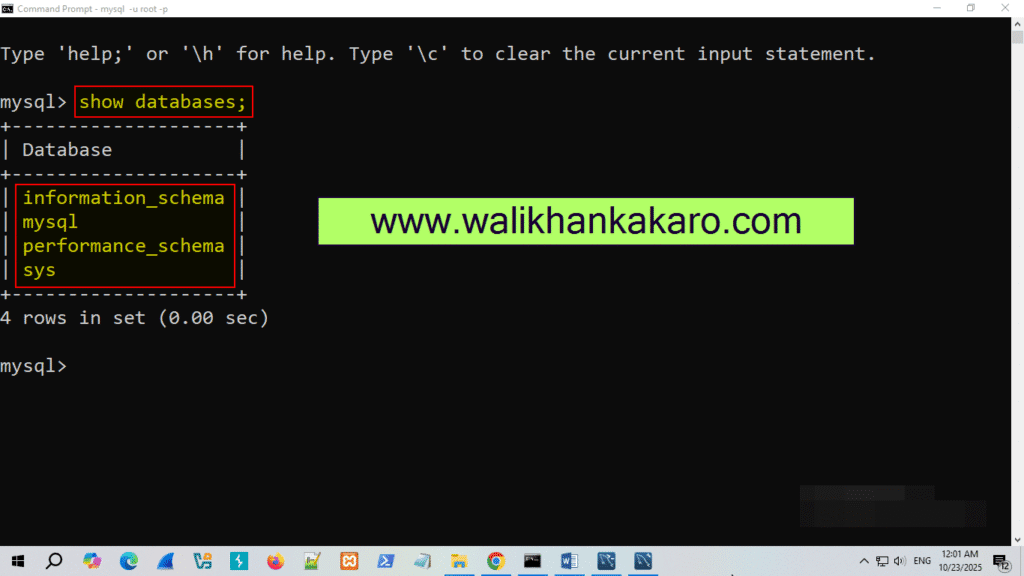
21: Create a new database.
Command: create database walikhankakar
22: To execute.
Command: ;
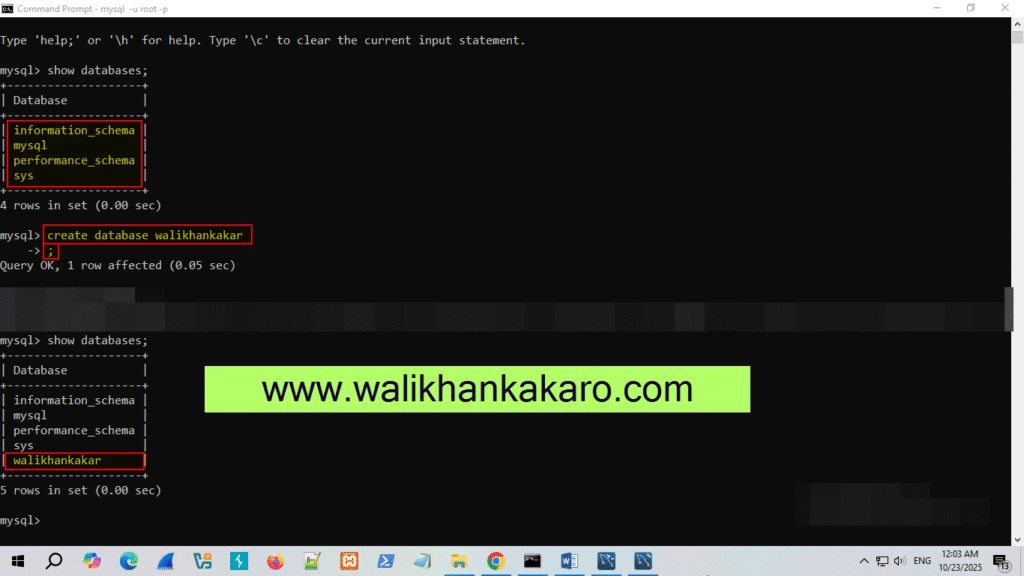
23: Open the walikhankakar database.
Command: use walikhankakar
Install MySQL on MacBook
1: Download the MySQL for MacBook Pro (Intel).
Website: https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/
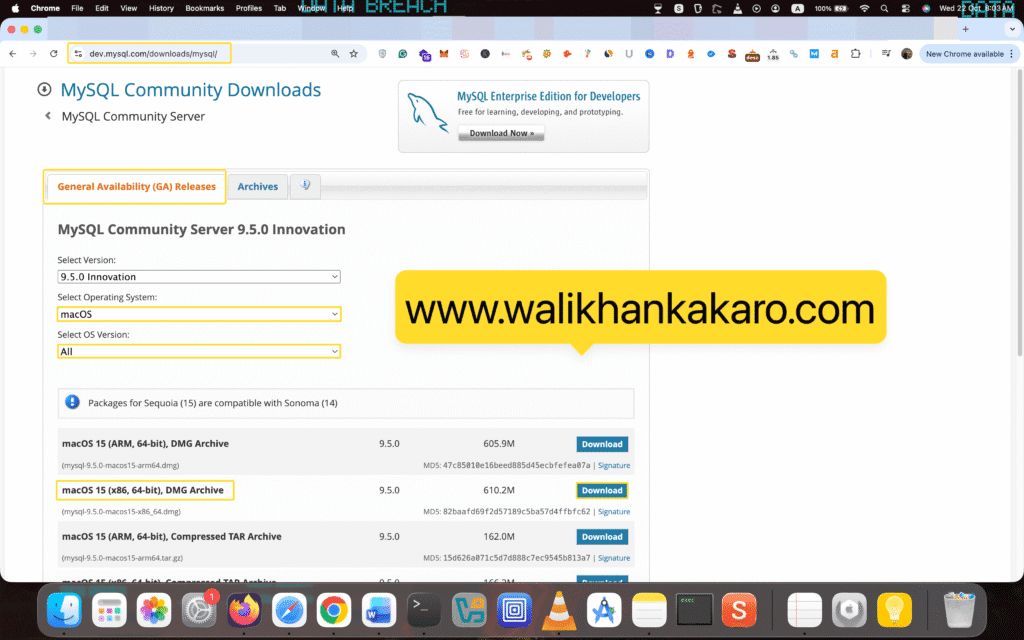
2: Install MySQL.
3: If you want to open or close MySQL, go to the System Settings (In the MacBook Pro).

4: Download the MySQL Workbench.
Website: https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/workbench/
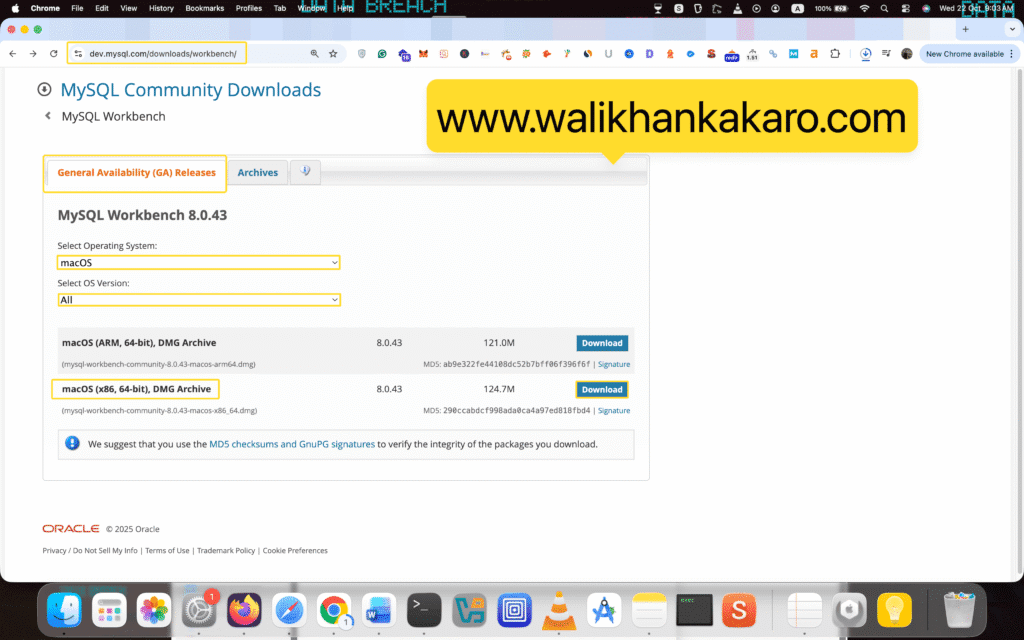
5: Drag and drop the MySQL Workbench.
6: Install the MySQL Workbench.

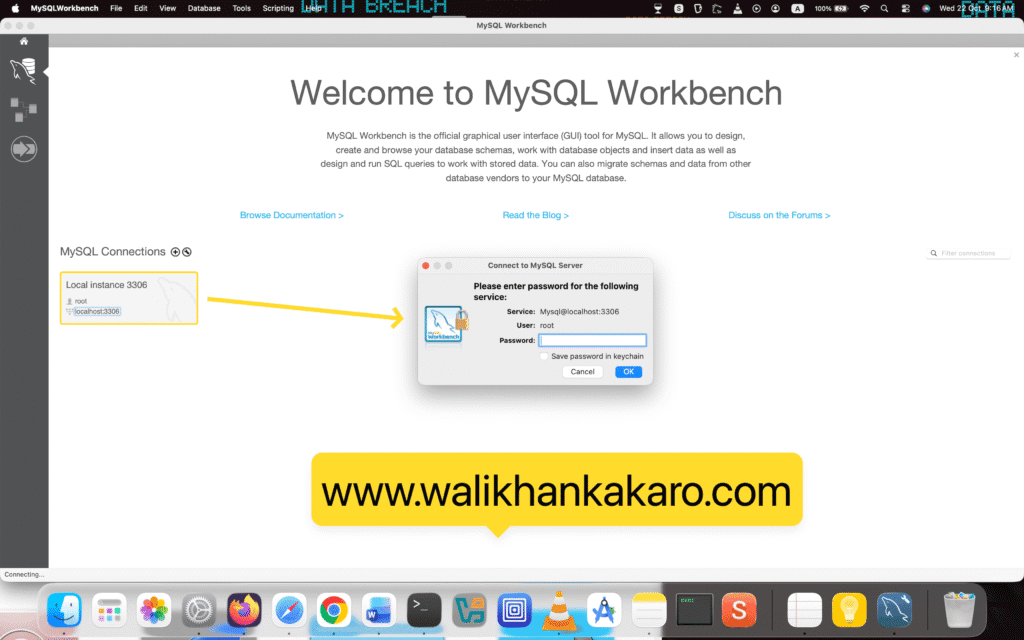
7: Log in to the Localhost.
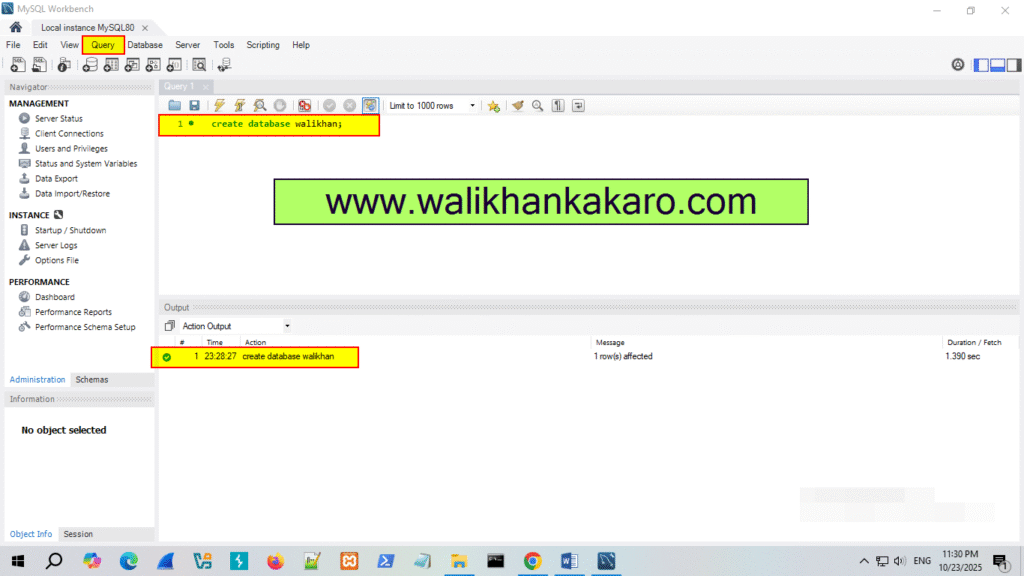
How to create a database with MySQL Workbench
1: Open the MySQL Workbench.
2: Create a new database in the MySQL Workbench.
Command: create database walikhan;
3: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
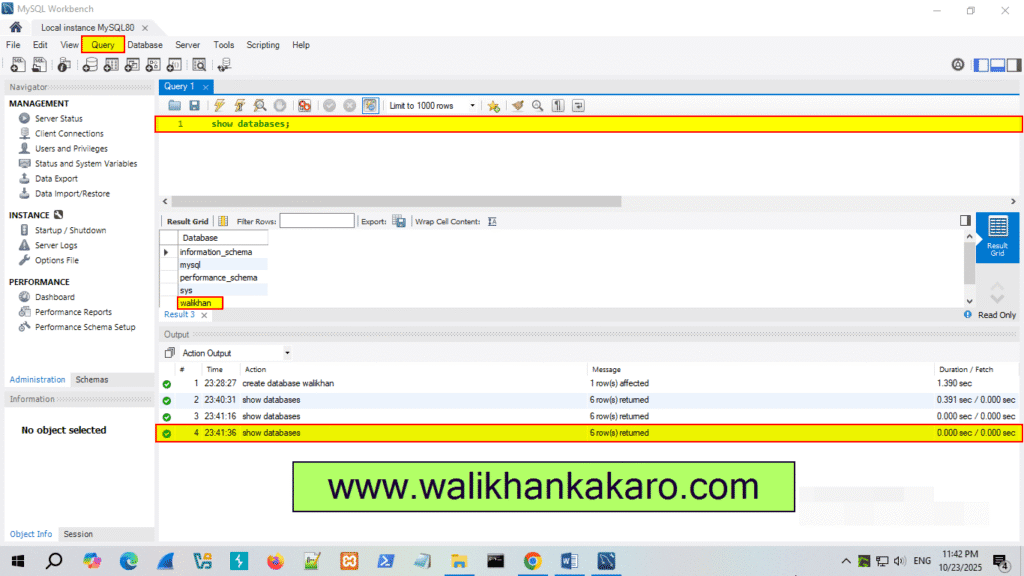
4: Check the Databases.
Command: show databases;
5: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
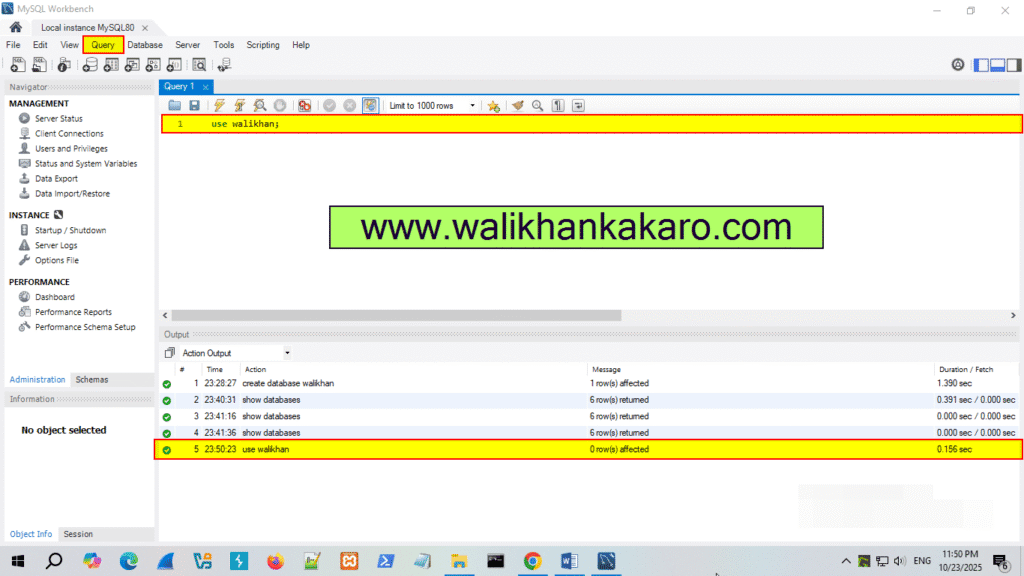
6: Open the walikhan Database.
Command: use walikhan;
7: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
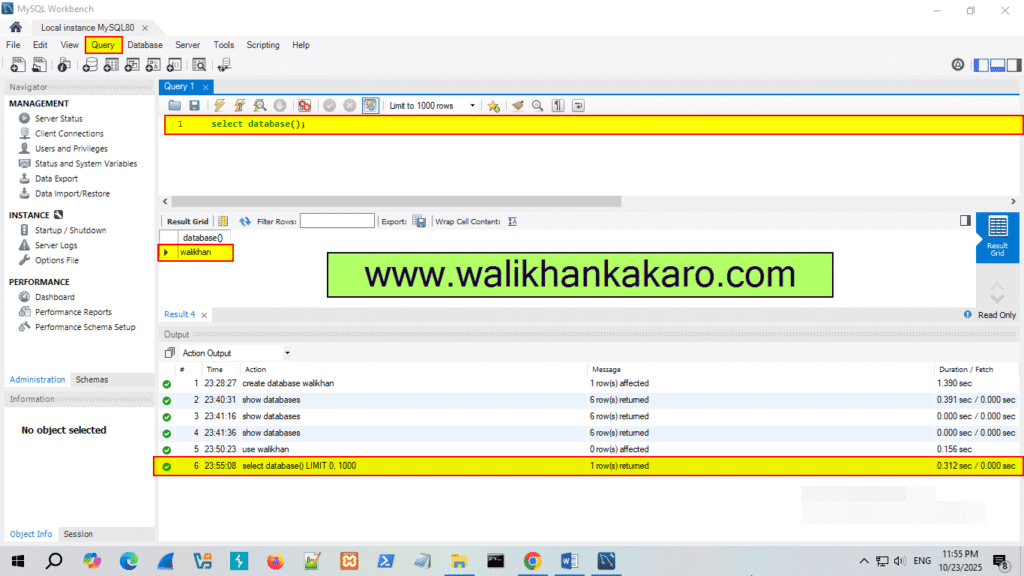
8: Check the current Database.
Command: select database();
9: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
How to create a Table in MySQL
1: What is a database Table?
Answer: A Database table is a collection of rows and columns that contains relational data.
| Id | DOB | |
| 1 | walikhan@gmail.com | 10.10.1990 |
| 2 | wali@gmail.com | 11.11.1999 |
| 3 | kakar@gmail.com | 10.1.1960 |
2: Open the MySQL Workbench.
3: Select the Schemas.
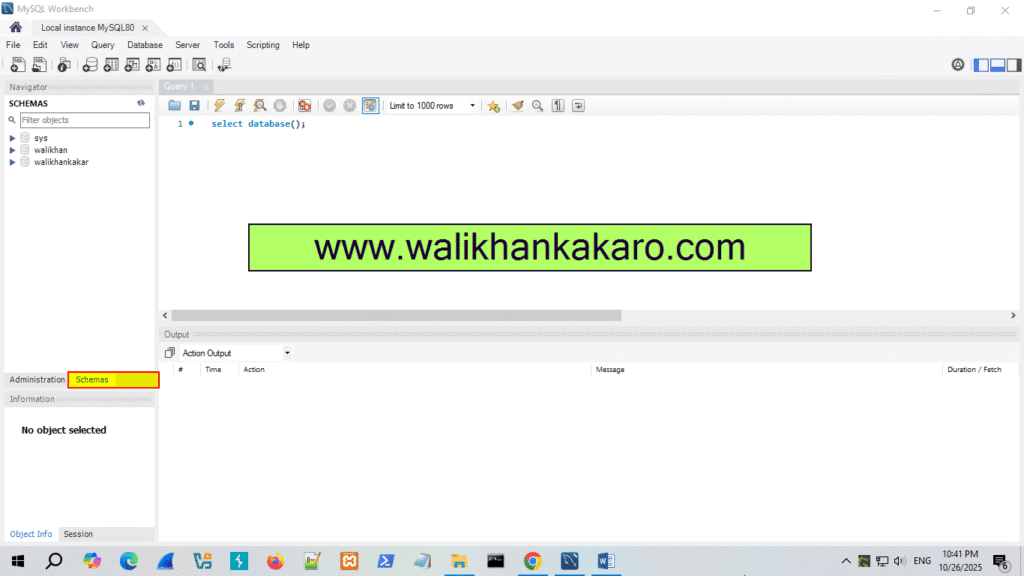
4: Use the walikhankakar Database.
Command: use walikhankakar
5: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
6: Categories of Datatypes:
1: Sting (walikhankakar).
2: Numeric (25).
3: Data and Time (10.10.1990).
7: String Data Types:
1: CHAR (size) 0 to 255.
2: VARCHAR (size) 0 to 65535.
3: BINARY (size).
4: VARBINARY (SIZE).
5: TINYTEXT 255 characters.
6: TEXT (size) 65,535 bytes.
7: MEDIUMTEXT 16,777,215 characters.
8: LONGTEXT 4,294,967,295 characters.
9: TINYBLOB 255 bytes.
10: BLOB (size) 65,535 bytes.
11: MEDIUMBLOB 16,777,295 bytes.
12: LONGBLOB 4,294,967, 295 bytes.
13: ENUM (va1i, va2, va13, …) list up to 65535 values.
14: SET (va1i, va12, va13, …) list up to 64 values.
8: Number Data Types:
1: BIT (size) 1 to 64.
2: TINYINT (size) -128 to 127.
3: INT (size) -2147483648 to 2147483647.
4: INTEGER (size).
5: SMALLINT (size) -32768 to 32767.
6: MEDIUMINT (size) -8388608 to 8388607.
7: BIGINT (size) -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807.
8: BOOL.
9: BOOLEAN 0/1.
10: FLOAT (p).
11: DOUBLE (size, d) 255.568.
12: DECIMAL (size, d) Size = 60, d = 30.
13: DEC (size, d)
9: Date Data Types:
1: DATE ‘1000-10-10’ to ‘9999-12-31’
2: DATETIME (fsp) YYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss
3: TIMESTAMP (fsp).
4: TIME (fsp) hh:mm:ss
5: YEAR four-digit format: 1901
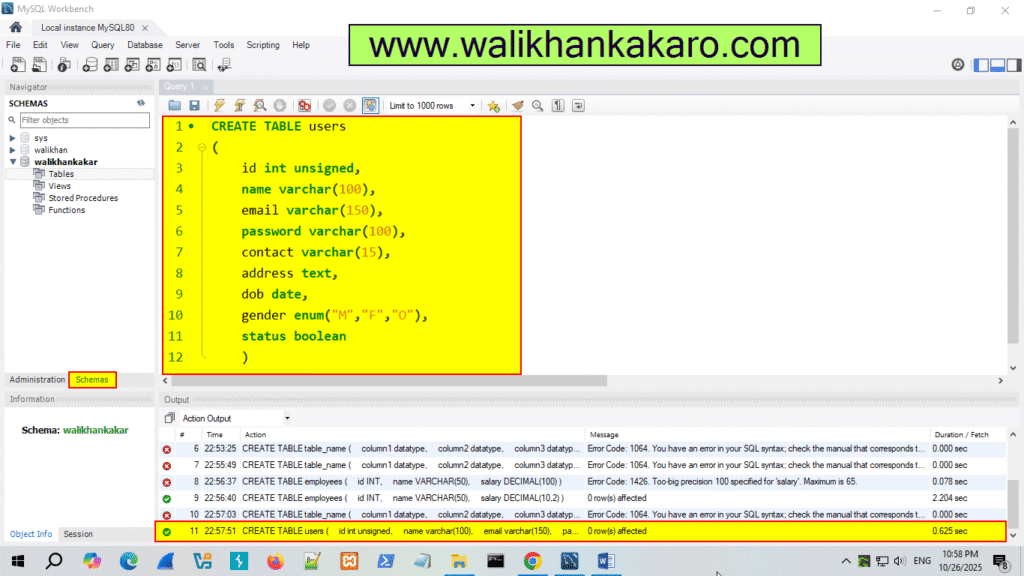
10: Create a Table for users.
Code: CREATE TABLE users
(
id int unsigned,
name varchar(100),
email varchar(150),
password varchar(100),
contact varchar(15),
address text,
dob date,
gender enum(“M”,”F”,”O”),
status boolean
)
11: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
How to add data into mysql table
1: Open the MySQL Workbench.
2: Go into the walikhankakar Database.
Command: use walikhankakar
3: Insert the Data into a Table.
Code: INSERT INTO users
(id,name,email,password,contact, address,dob,gender,status)
VALUES
(1,”Walikhan”,”walikhan@gmail.com”,”walikhan1234″,”Kakaristan”,”033312569″,”1999-10-10″,”M”,1)
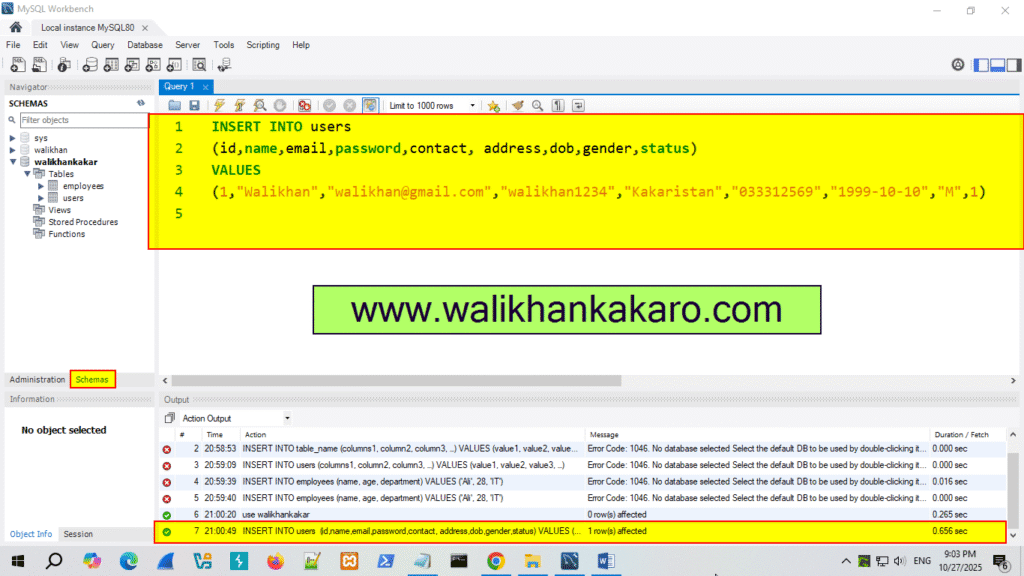
4: Run the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
5: Insert the multiple data into the table.
Code: INSERT INTO users
(id,name,email,password,contact, address,dob,gender,status)
VALUES
(1,”Walikhan”,”walikhan@gmail.com”,”walikhan1234″,”Kakaristan”,”033312569″,”1999-10-10″,”M”,1),
(2,”Wali”,”wali@gmail.com”,”wali1234″,”Kaka”,”033312569″,”1999-10-10″,”M”,1),
(3,”Walikhankakar”,”walikhankakar@gmail.com”,”walikhankakar1234″,”Kakaristan”,”033312569″,”1999-10-10″,”M”,1)
6: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
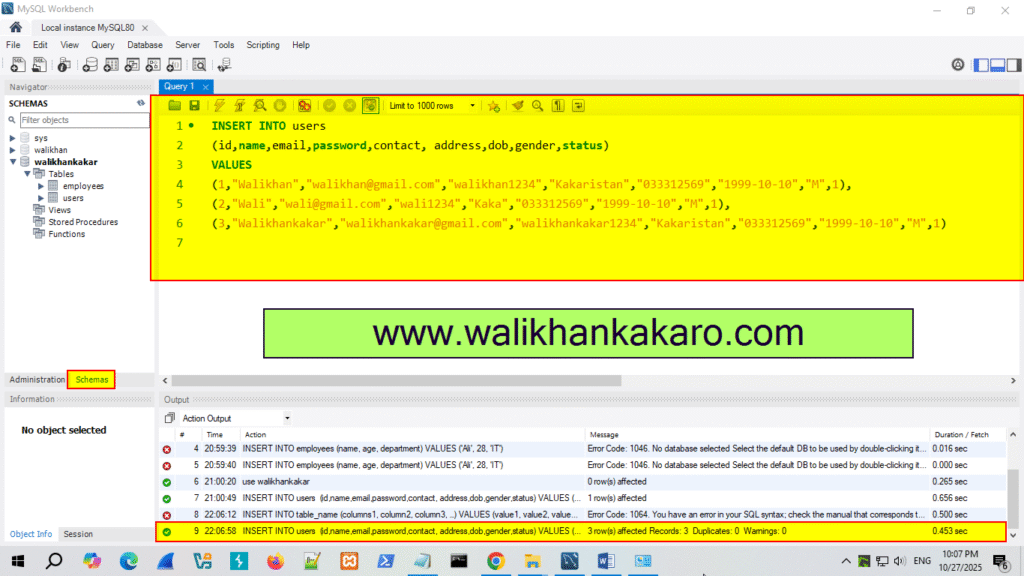
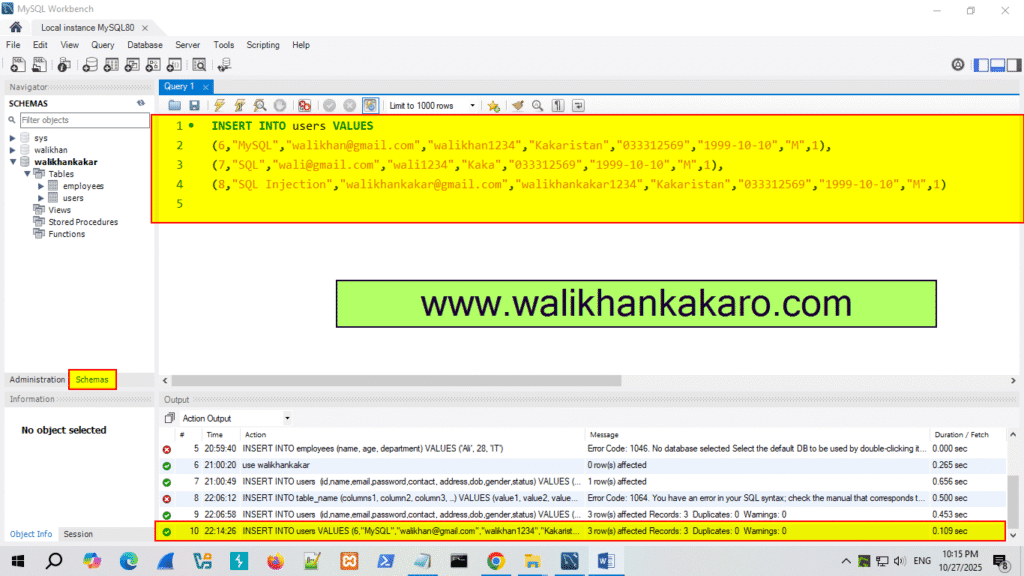
7: You can insert multiple data items also like this.
Code: INSERT INTO users VALUES
(6,”MySQL”,”walikhan@gmail.com”,”walikhan1234″,”Kakaristan”,”033312569″,”1999-10-10″,”M”,1),
(7,”SQL”,”wali@gmail.com”,”wali1234″,”Kaka”,”033312569″,”1999-10-10″,”M”,1),
(8,”SQL Injection”,”walikhankakar@gmail.com”,”walikhankakar1234″,”Kakaristan”,”033312569″,”1999-10-10″,”M”,1)
8: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
MySQL select query with where clause
1: Open the MySQL Workbench.
2: Select the Database.
Command: use walikhankakar
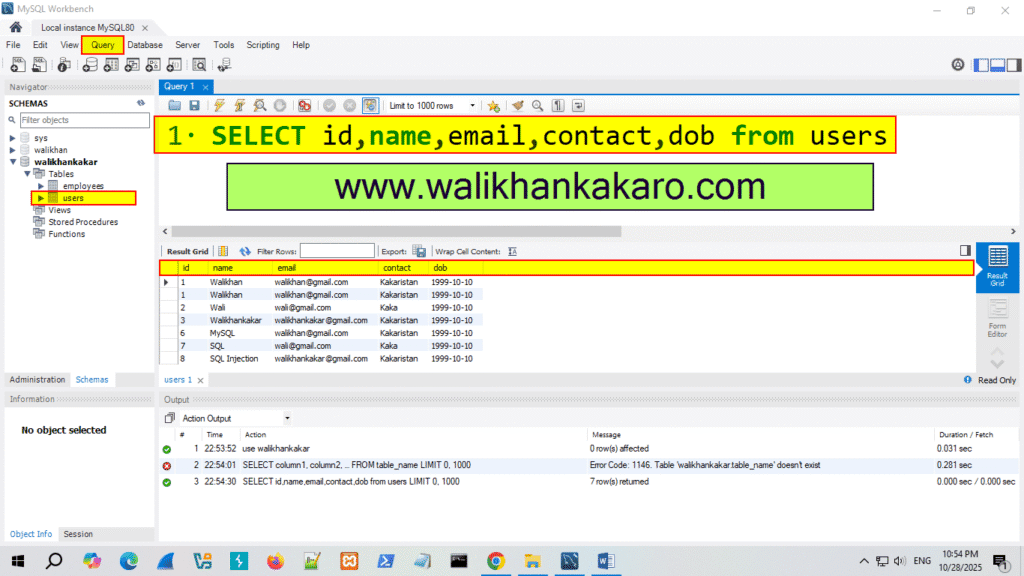
3: Check the table query.
Code: SELECT id,name,email,contact,dob from users
5: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
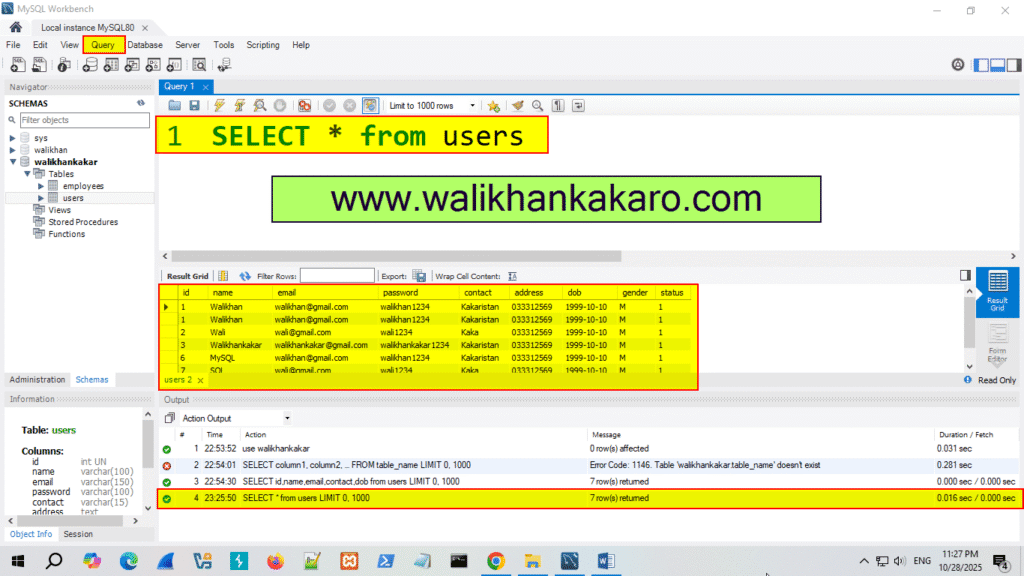
6: Select all the columns.
Code: SELECT * from users
7: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
8: What is Where clause.
Answer: The WERE clause is used to filter records.
It is used to extract only those records that fulfill a specified condition.
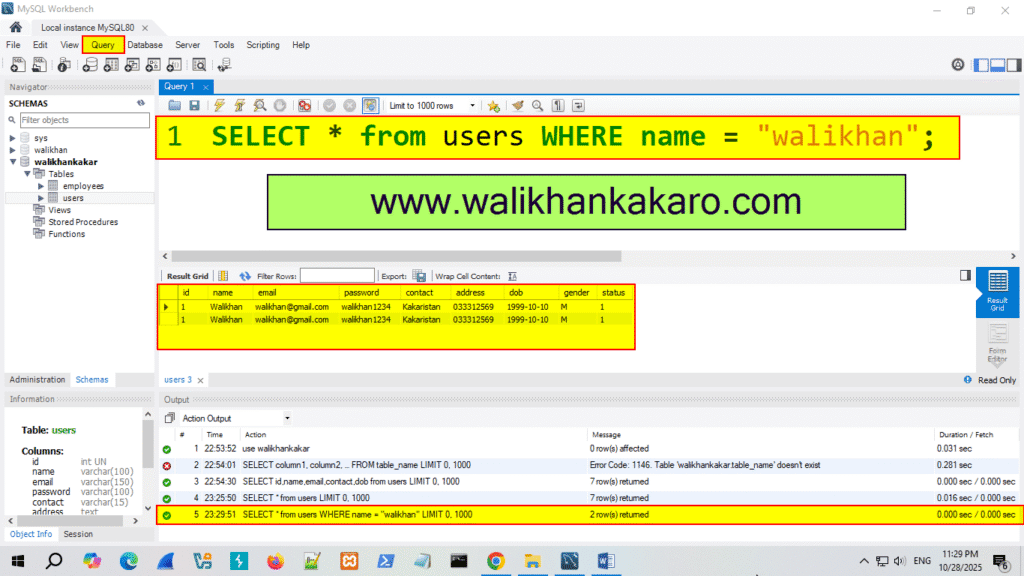
9: Check only the specific names.
Code: SELECT * from users WHERE name = “walikhan”;
10: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
MySQL table constraints
1: Open the MySQL Workbench.
2: MySQL constraints:
1: NOT NULL
2: UNIQUE
3: DEFAULT
4: CHECK
5: FOREGIN KEY
6: PRIMARY KEY
3: Table without constraints.
| Id | Name | Age | Gender | Phone | Status |
| 1 | A | 17 | M | 3269 | 1 |
| 2 | B | 20 | F | 5862 | 1 |
| 3 | C | 30 | M | 3269 | 1 |
| D | 25 | M | 2039 | 1 | |
| 4 | E | 23 | M | 1096 | 1 |
4: Use a Database.
Code: use walikhankakar;
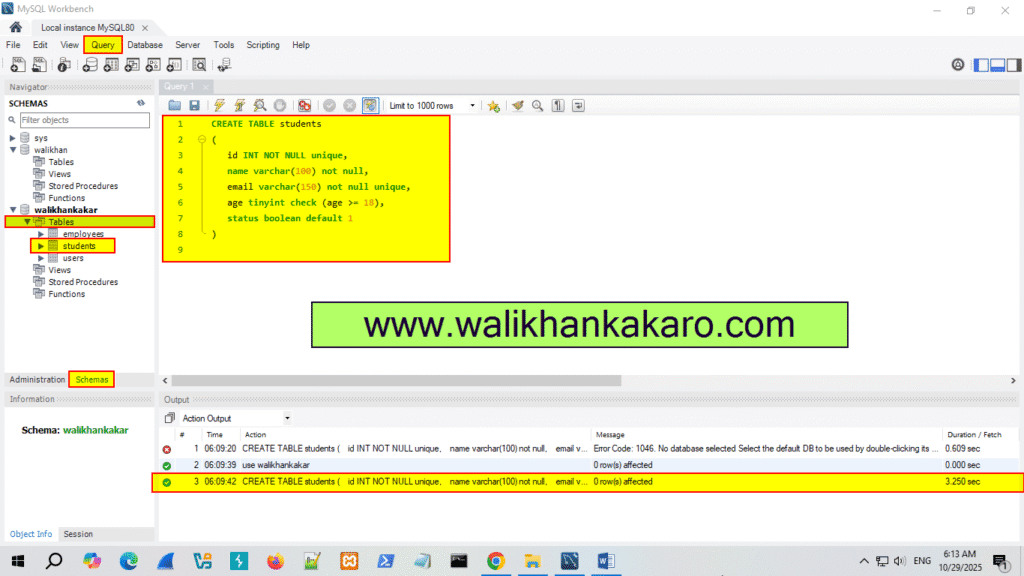
5: Create a new table.
Code: CREATE TABLE students
(
id INT NOT NULL unique,
name varchar(100) not null,
email varchar(150) not null unique,
age tinyint check (age >= 18),
status boolean default 1
)
6: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
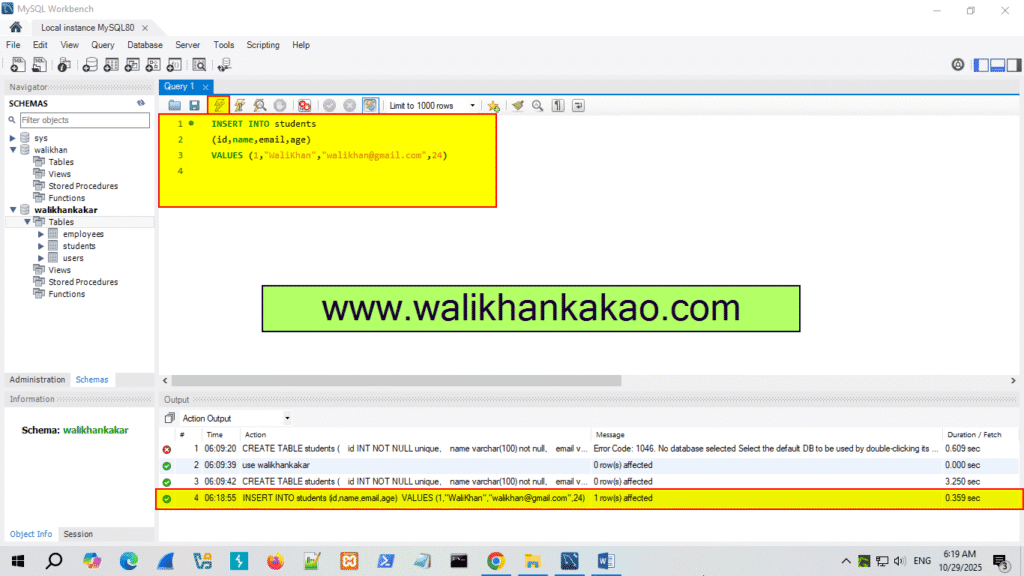
7: Insert the data into the students table.
Code: INSERT INTO students
(id,name,email,age)
VALUES (1,”WaliKhan”,”walikhan@gmail.com”,24)
8: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
and or not operator
AND, OR and NOT:
1: AND operator: MySQL logical AND operator compares two expressions and returns true if both of the expressions are true.
2: OR operator: MYSQL OR operator compares two expressions and returns TRUE if either of the expressions is TRUE.
3: NOT operator: MySQL NOT operator reverses or negates the input.
1: Open the MySQL Workbench.
2: Select the Database.
Command: use walikhankakar
3: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
MySQL IN operator
IN operator:
The IN operator allows you to specify multiple values in a WHERE clause.
The IN operator is a shorthand for multiple OR candidates.
IN operator Syntax:
Code: SELECT * FROM table_name
WHERE column_name IN (value1, value2, …);
MySQL wildcard
MySQL LIKE:
MySQL LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column.
1: The percent sign (%) represents zero, one, or multiple characters.
2: The underscore sign (_) represents one, single character.
Patterns:
| LIKE Operator | Description |
| LIKE ‘a%’ | Starts with “a” |
| LIKE ‘%a’ | End with “a” |
| LIKE ‘%or%’ | Have “or” in any position. |
| LIKE ‘_r%’ | Have “r” in the second position. |
| LIKE ‘a_%’ | Starts with “a” and are at least 2 characters in length. |
| LIKE ‘a__%’ | Starts with “a” and are at least 3 characters in length. |
| LIKE ‘a%0’ | Starts with “a” and ends with “0” |
1: Open the MySQL Workbench.
2: Select the Database.
Command: use walikhankakar
3: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
4: Create a new Table.
Code: CREATE TABLE student (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
email VARCHAR(255),
age INT,
city VARCHAR(100),
gender ENUM(‘Male’, ‘Female’, ‘Other’),
status ENUM(‘Active’, ‘Inactive’, ‘Graduated’)
);
5: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
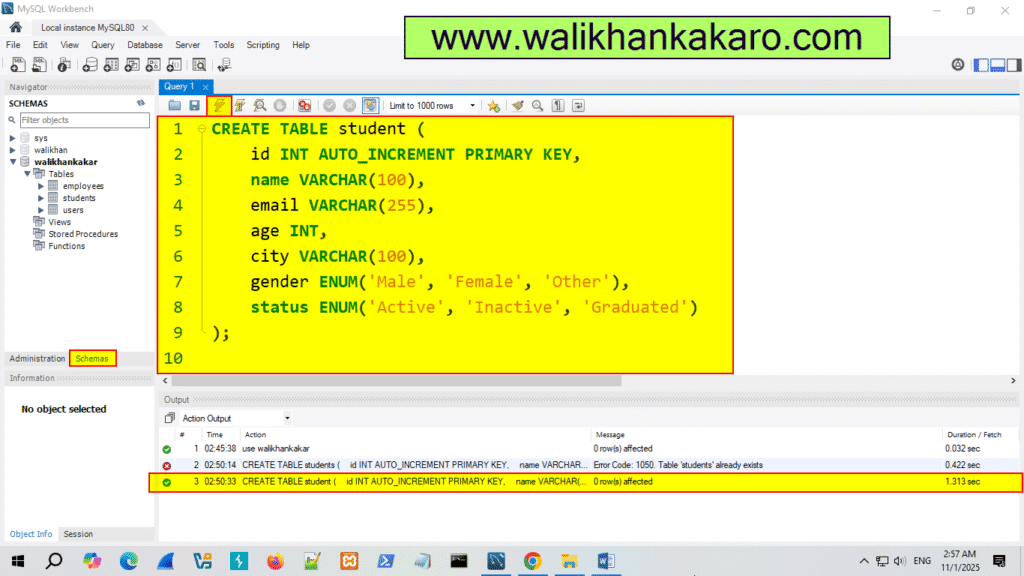
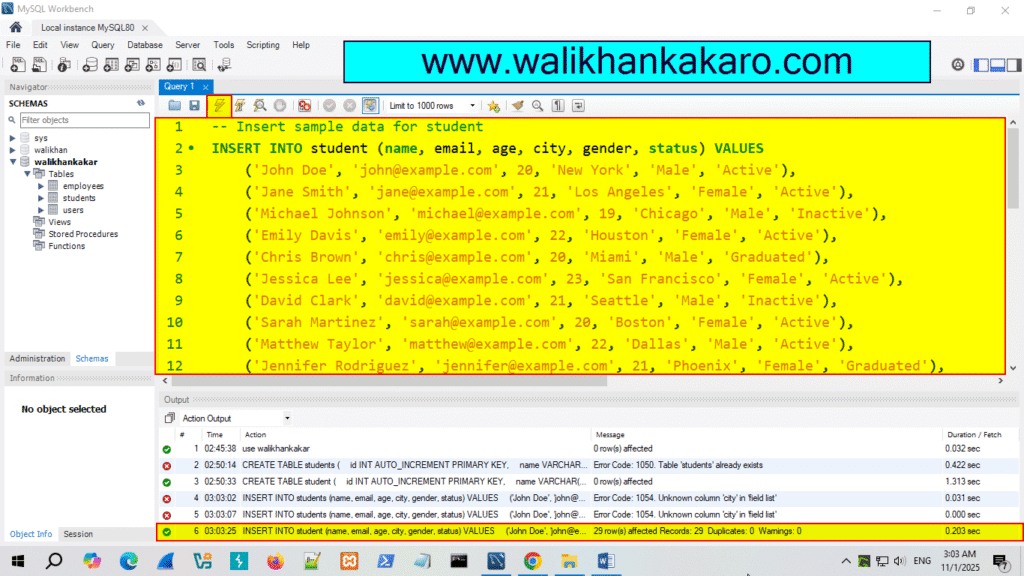
6: Insert the Data into the students.
Code: — Insert sample data for student
INSERT INTO student (name, email, age, city, gender, status) VALUES
(‘John Doe’, ‘john@example.com’, 20, ‘New York’, ‘Male’, ‘Active’),
(‘Jane Smith’, ‘jane@example.com’, 21, ‘Los Angeles’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘Michael Johnson’, ‘michael@example.com’, 19, ‘Chicago’, ‘Male’, ‘Inactive’),
(‘Emily Davis’, ’emily@example.com’, 22, ‘Houston’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘Chris Brown’, ‘chris@example.com’, 20, ‘Miami’, ‘Male’, ‘Graduated’),
(‘Jessica Lee’, ‘jessica@example.com’, 23, ‘San Francisco’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘David Clark’, ‘david@example.com’, 21, ‘Seattle’, ‘Male’, ‘Inactive’),
(‘Sarah Martinez’, ‘sarah@example.com’, 20, ‘Boston’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘Matthew Taylor’, ‘matthew@example.com’, 22, ‘Dallas’, ‘Male’, ‘Active’),
(‘Jennifer Rodriguez’, ‘jennifer@example.com’, 21, ‘Phoenix’, ‘Female’, ‘Graduated’),
(‘Daniel Anderson’, ‘daniel@example.com’, 20, ‘Austin’, ‘Male’, ‘Active’),
(‘Laura Wilson’, ‘laura@example.com’, 22, ‘Denver’, ‘Female’, ‘Inactive’),
(‘James Garcia’, ‘james@example.com’, 21, ‘San Diego’, ‘Male’, ‘Active’),
(‘Amanda Harris’, ‘amanda@example.com’, 22, ‘Portland’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘Ryan Martin’, ‘ryan@example.com’, 20, ‘Atlanta’, ‘Male’, ‘Graduated’),
(‘Stephanie Thompson’, ‘stephanie@example.com’, 23, ‘Philadelphia’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘Robert Jackson’, ‘robert@example.com’, 21, ‘Detroit’, ‘Male’, ‘Inactive’),
(‘Rachel White’, ‘rachel@example.com’, 20, ‘Minneapolis’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘Christopher Martinez’, ‘christopher@example.com’, 22, ‘San Jose’, ‘Male’, ‘Active’),
(‘Emily Taylor’, ’emilyt@example.com’, 21, ‘Las Vegas’, ‘Female’, ‘Graduated’),
(‘Joshua Hernandez’, ‘joshua@example.com’, 20, ‘Salt Lake City’, ‘Male’, ‘Active’),
(‘Megan King’, ‘megan@example.com’, 23, ‘Charlotte’, ‘Female’, ‘Inactive’),
(‘Justin Lee’, ‘justin@example.com’, 20, ‘Tampa’, ‘Male’, ‘Active’),
(‘Melissa Scott’, ‘melissa@example.com’, 22, ‘Orlando’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘Kevin Walker’, ‘kevin@example.com’, 21, ‘Nashville’, ‘Male’, ‘Graduated’),
(‘Hannah Green’, ‘hannah@example.com’, 20, ‘Kansas City’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘Brandon Young’, ‘brandon@example.com’, 23, ‘Cleveland’, ‘Male’, ‘Inactive’),
(‘Olivia Perez’, ‘olivia@example.com’, 21, ‘Pittsburgh’, ‘Female’, ‘Active’),
(‘Tyler Harris’, ‘tyler@example.com’, 22, ‘St. Louis’, ‘Male’, ‘Active’);
7: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
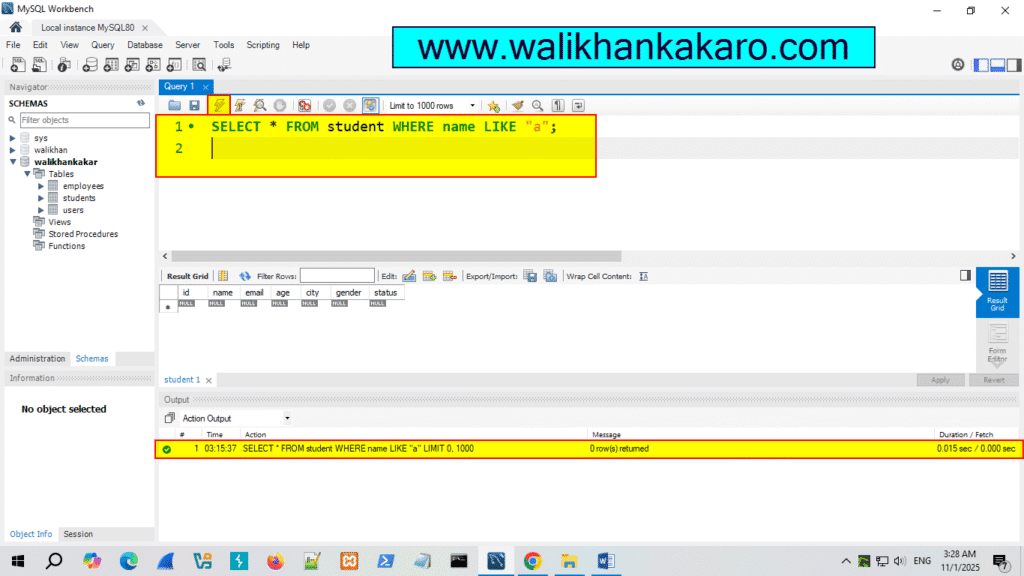
8: Check the name that starts with A.
Code: SELECT * FROM student WHERE name LIKE “a”;
9: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
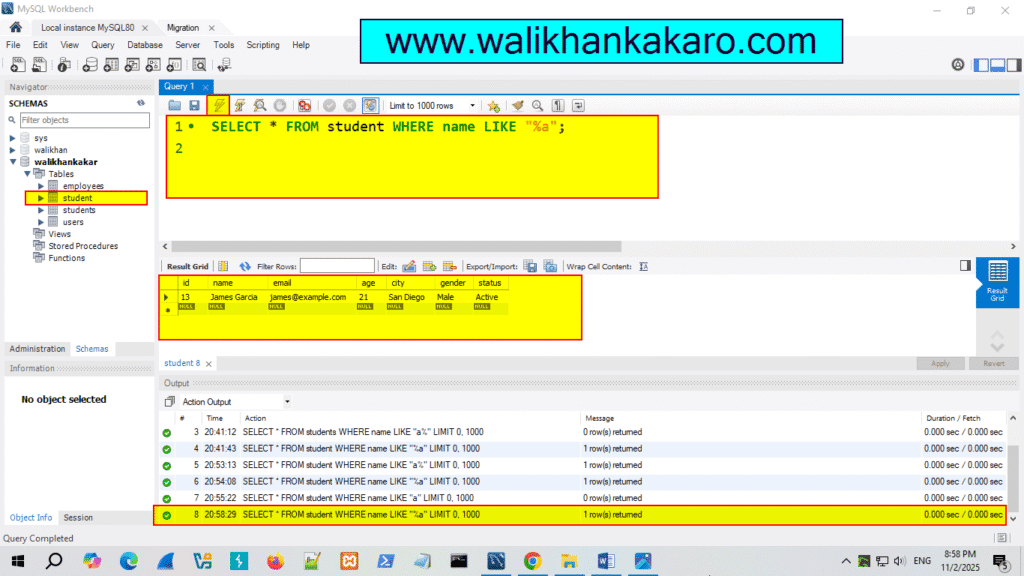
10: Check the names that end with A.
Code: SELECT * FROM student WHERE name LIKE “%a”;
11: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
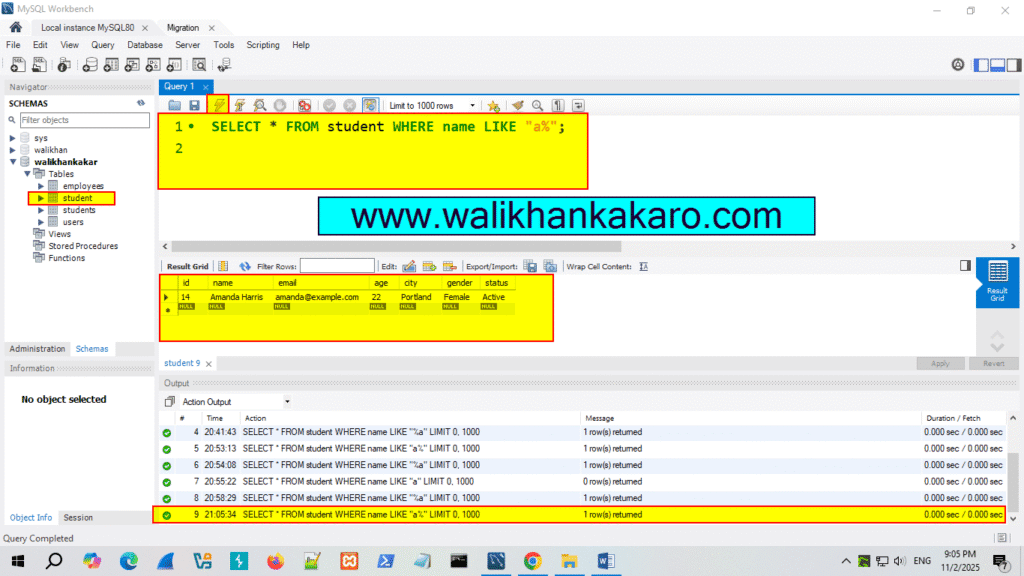
12: Check the names that start with the letter A.
Code: SELECT * FROM student WHERE name LIKE “a%”;
13: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
14: Check the names at the start, in the middle, or at the end.
Code: SELECT * FROM student WHERE name LIKE “%a%”;
15: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter

mysql between and not between
1: Open the MySQL Workbench.
2: Go to your Database.
Code: use walikhankakar
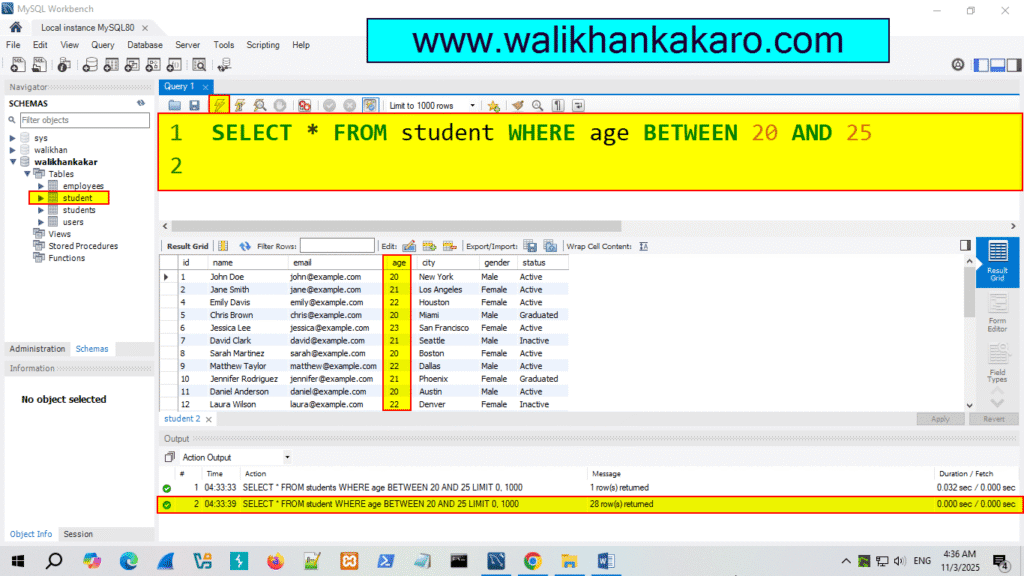
3: Check the age, where the age is between 20 to 25.
Code: SELECT * FROM student WHERE age BETWEEN 20 AND 25
4: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
distinct and order by in SQL
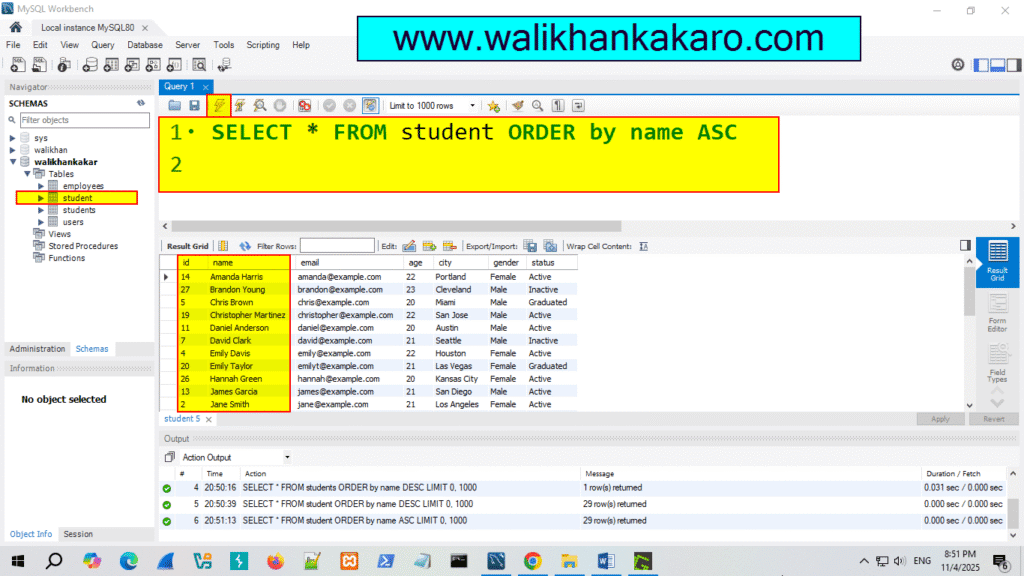
1: Open the MySQL Workbench.
2: Check the names in the Ascending style.
Code: SELECT * FROM student ORDER by name ASC
3: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
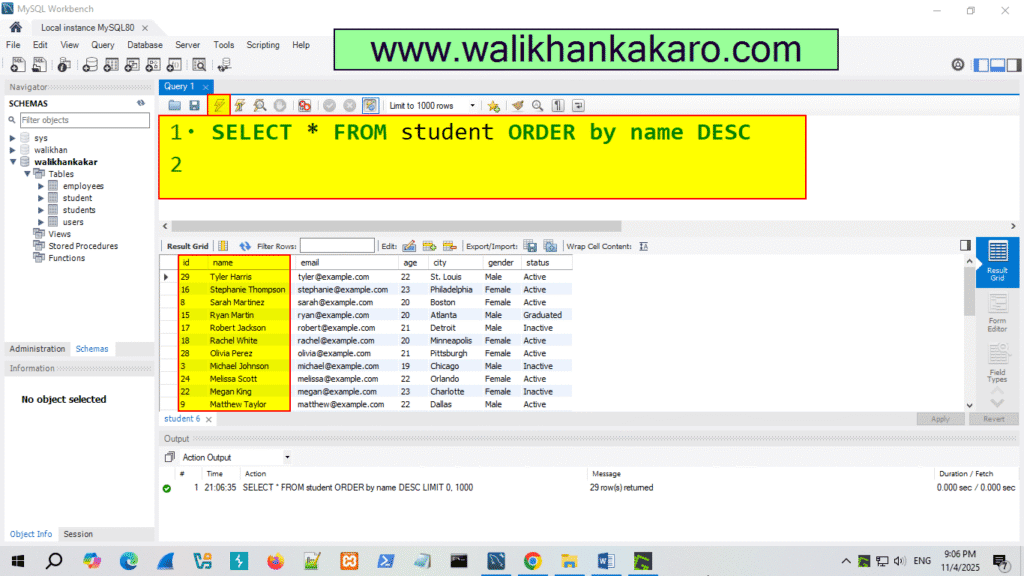
4: Check the names in the Descending style.
Code: SELECT * FROM student ORDER by name DESC
5: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
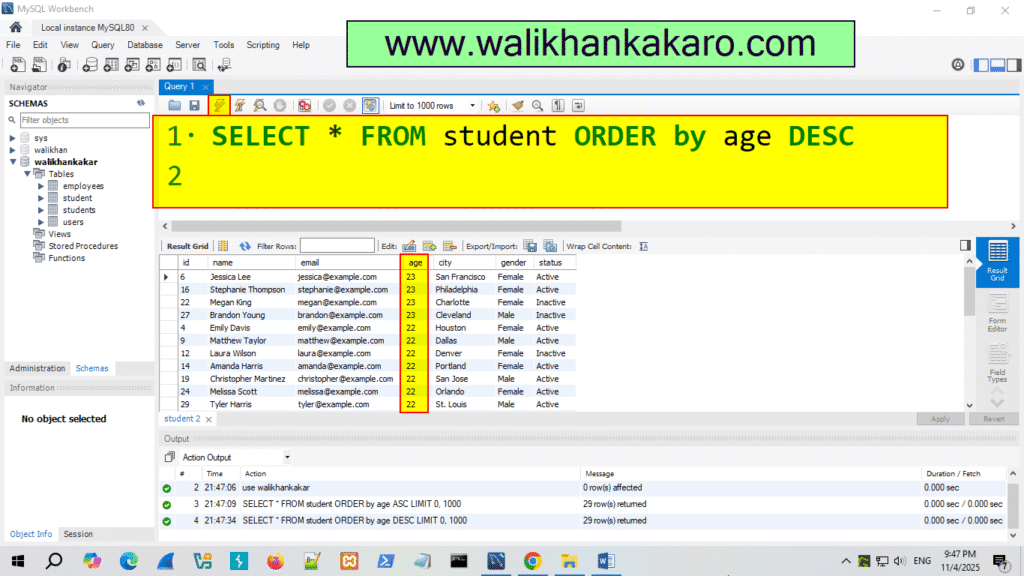
6: Same procedure for age.
Ascending style Code: SELECT * FROM student ORDER by age ASC
Descending style Code: SELECT * FROM student ORDER by age DESC
7: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
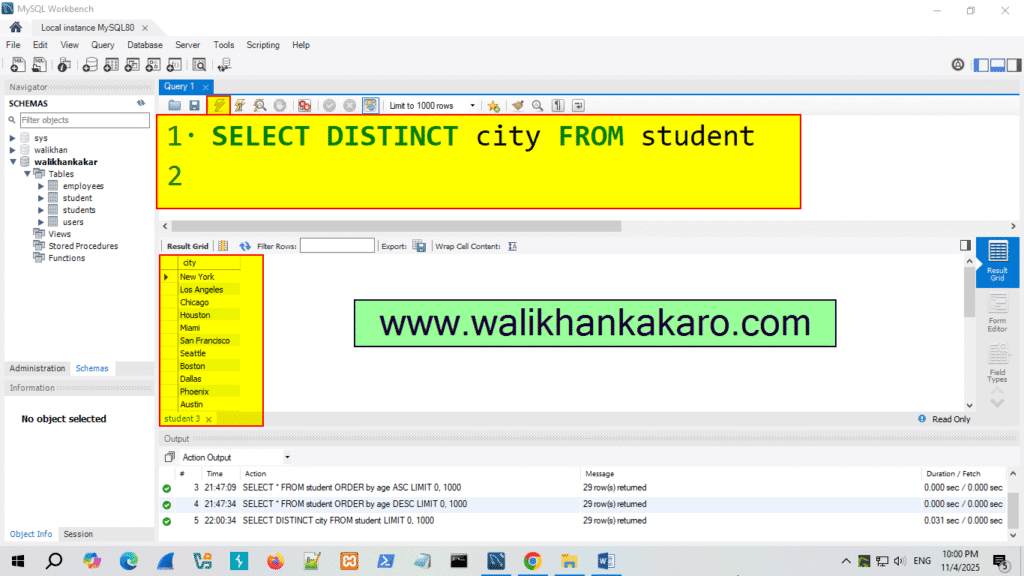
8: Check the unique city names.
Code: SELECT DISTINCT city FROM student
9: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
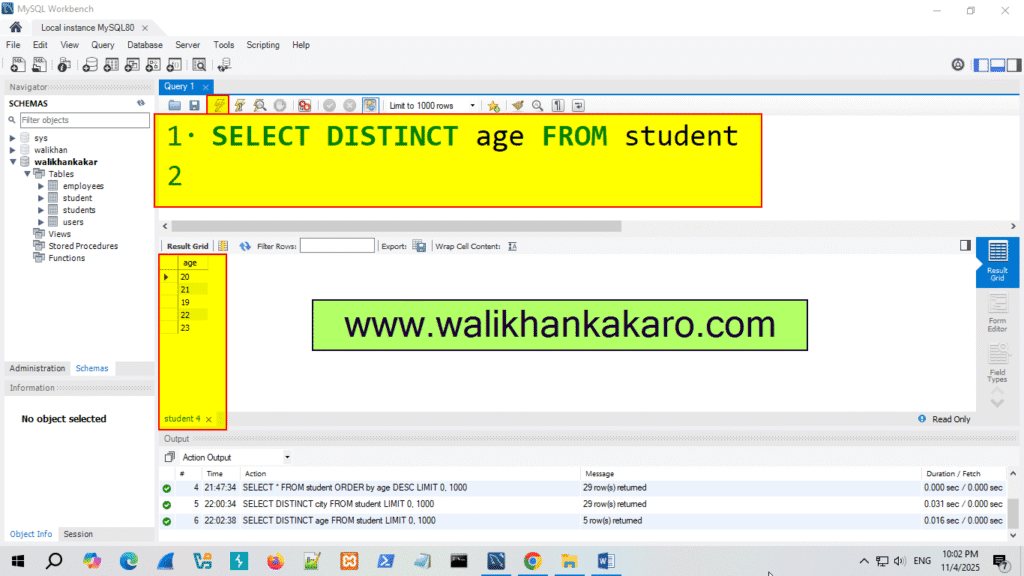
10: Check the Unique age.
Code: SELECT DISTINCT age FROM student
11: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
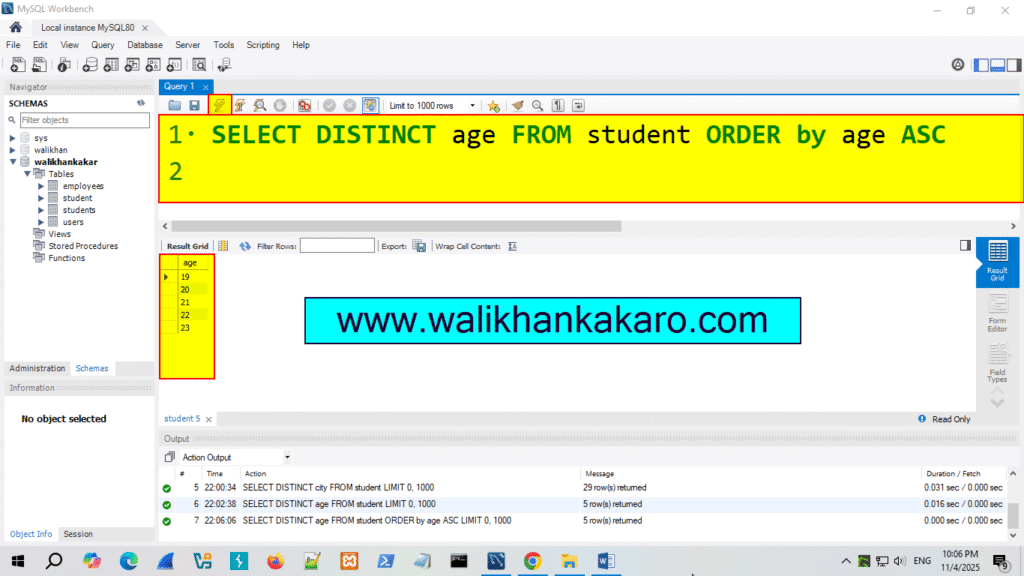
12: Check the age by the Ascending style.
Code: SELECT DISTINCT age FROM student ORDER by age ASC
13: Execute the command.
Shortcut key: Ctrl + Enter
MySQL aggregate function
1: COUNT (): Returns the number of rows in a database table.
2: SUM (): Returns the total sum of a numeric column.
3: AVG (): Calculate the average of a set of values.
4: MIN (): Returns the lowest value (minimum) in a set of non-NULL values.
5: MAX (): Returns the greatest value (maximum) in a set of non-NULL values.


